您当前的位置:检测资讯 > 科研开发
嘉峪检测网 2022-07-08 11:36
理想的骨修复材料除具备良好的生物学活性与力学性能外,还应具备内部连通的多孔结构与个性化的几何外观。本研究采用选择性激光熔化技术制备了力学性能适配的3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr骨修复支架,并通过体内外实验研究其生物安全性与抗菌性能。
01、研究内容简介
金属植入物被广泛应用于骨科领域。植入物感染是骨科手术后最严重的并发症之一。传统上,植入物感染的治疗方案包括手术清创、全身抗生素治疗和局部抗生素治疗等,将不可避免地导致二次手术及各类并发症,也造成了严重的社会经济负担。因此,亟需研发一种具备抗感染性能的骨植入物材料用于预防和治疗此类感染。
鉴于其良好的生物相容性、骨诱导性和力学性能,可降解镁合金被视为新一代骨修复材料。既往研究表明,镁合金降解产生的碱性微环境具备广谱杀菌性能,可有效抑制革兰氏阳性及革兰氏阴性细菌的生长。因此,镁合金作为一种兼具抗菌和成骨性能的可生物降解材料,具有良好的临床转化前景。
理想的骨修复材料应具备内部连通的多孔结构与个性化的几何外观。目前,多孔镁合金植入物的主要制备方法包括熔模铸造法、粉末冶金法、溶体发泡法等方法,能够制备具有完全内部连通多孔结构的镁合金骨修复支架,但无法实现多孔镁合金内部孔隙结构的精准控制。近年来,金属增材制造技术的发展,为制备孔隙结构可调、内连通性可控的镁合金骨修复支架提供了新思路。然而,镁金属化学性质活泼,极易燃,采用激光或电子束制备3D打印镁合金存在诸多挑战,其体内生物学作用与功能亦未见报道。因此,我们团队通过医工交叉合作,采用选择性激光熔化技术,制备3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr骨修复支架,并通过体内外实验系统评估其抗菌性能与生物安全性,为3D打印镁合金植入物的研发与临床转化提供依据。
设计具有钻石型结构单元的多孔骨修复支架,支架设计孔径为400μm。支架设计完成后,导出slt格式打印文件,用于后续打印。通过气体雾化法成功制备了Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr镁合金粉末,粉末球型度高,平均粒径为63.9 ± 14.5μm,符合3D打印要求(Fig 1)。
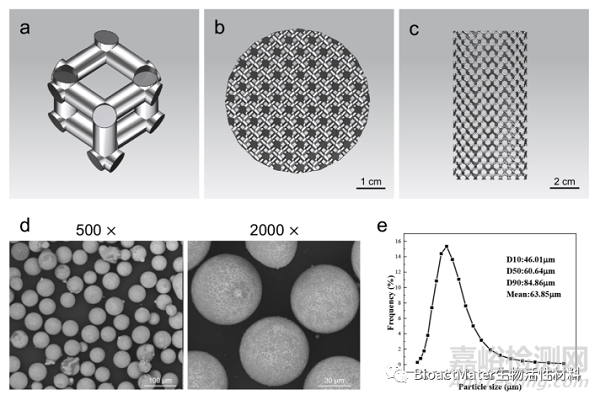
Fig. 1. Design of the 3D-printed JDBM implant and characterization of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr powder. a) Diamond unit cell. b) Top view of the computer-aided design model. c) Lateral view of the computer-aided design model. d) SEM image of the Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr powder. e) Particle size distribution of the Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr powder.
经后处理后,3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架多孔结构分布均匀,324.6±25.7μm,孔隙率为 52.1±1.6%。同时,通过体外浸泡实验,初步评价3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架的降解性能(Fig 2)。

Fig. 2. Characterization and degradation behavior of the 3D-printed JDBM implant. a) Surface morphology of the 3D-printed JDBM implants. b) Optical microscope images of 3D-printed JDBM implants. c) SEM images of as-fabricated and solid-solution-treated 3D-printed JDBM implant observed from side surfaces. d) Hydrogen release after immersing for 1–7 days. e) Mg2+ concentrations after immersing for 1–7 days.
体外实验结果表明,3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架具备良好的生物安全性与促成骨活性(Fig 3)。
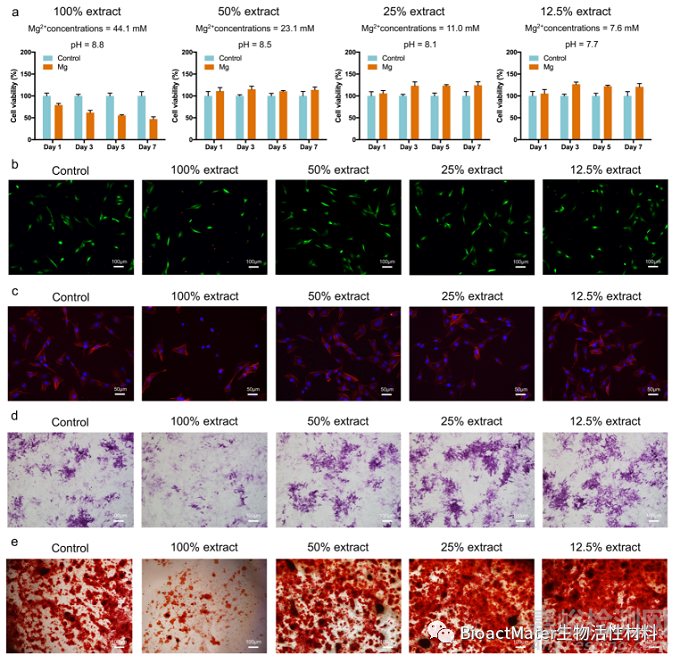
Fig. 3. Cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation in vitro. a) Cell viability, b) live/dead cells, and c) cell morphology of the MC3T3-E1 cells cultured with different extract concentrations. d) ALP staining after 7 d of culture. e) Alizarin red staining of cells cultured with different extract concentrations for 21 d.
3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架可显著抑制MRSA 粘附及细菌生物膜形成(Fig 4)。
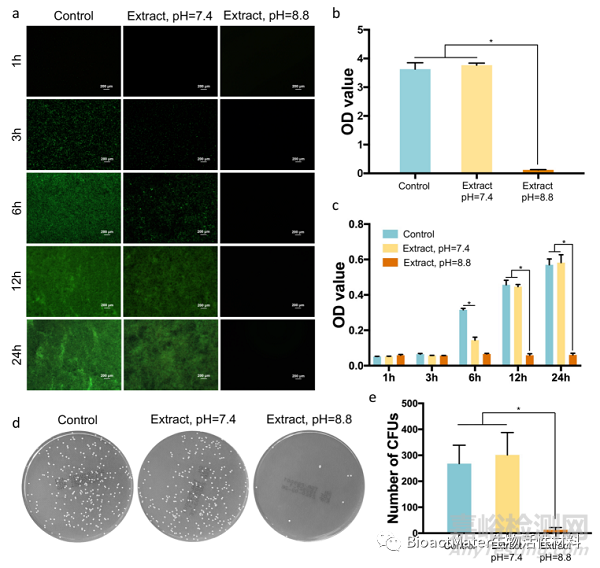
Fig. 4. Antibacterial activity of 3D-printed JDBM implants in vitro. a) Biofilm formation of MRSA cultured in different media after 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h of incubation. b) Absorption of crystal violet by MRSA biofilm after 24 h of incubation. c) Semi-quantitative analysis of bacterial concentration after 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h of in- cubation. d) Representative images of MRSA cultured in different media. e) Statistical analysis of colony number after 24 h of incubation. *p < 0.05.
动物实验结果表明,3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架可有效预防植入物感染形成(Fig 5)。
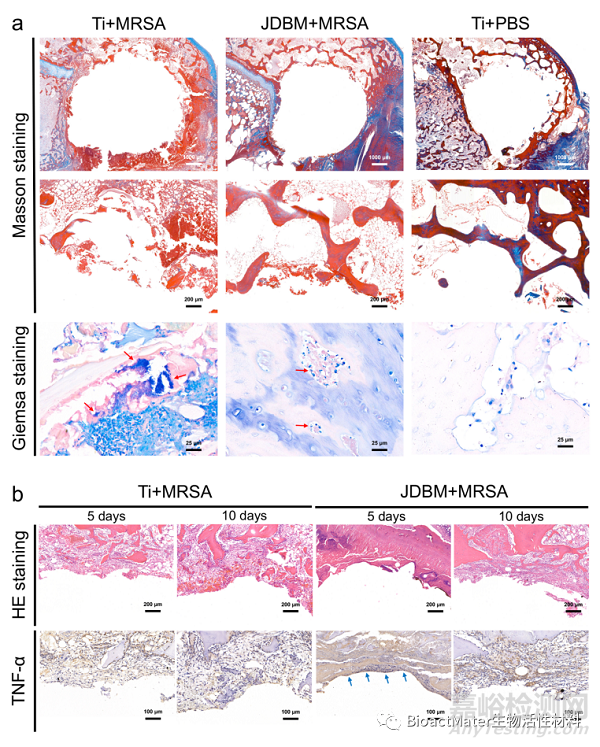
Fig. 5. Histological evaluation of implant-related infection. a) Masson and Giemsa staining of peri-implant tissue at four weeks after implantation. b) HE staining and immunohistochemical detection of TNF-α secretion at the bone-implant interface at 5 and 10 days after implantation.
此外,3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架具备良好的生物安全性。3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架植入后,实验动物心、肝、脾、肺、肾未见 明显组织学异常改变(Fig 6),实验动物主要脏器镁离子含量未见异常升高(Table 1)。
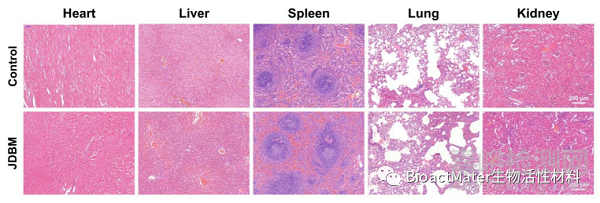
Fig. 6. Evaluation of organizational microstructures of the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney with HE staining.
Table 1 Results of blood tests of experimental animal at 4 weeks after implantation.
|
Cr |
ALT |
AST |
ALB |
A/G |
|
|
Control |
69.2 9.2 |
39.8 .4 |
21.1 |
49.3 |
2.2 |
|
JDBM |
76.6 9.4 |
37.4 9.7 |
21.2 4.5 |
47.4 |
2.5 |
|
p value |
0.363 |
0.771 |
0.972 |
0.652 |
0.710 |
|
Cr |
ALT |
AST |
ALB |
A/G |
|
|
Control |
69.2 9.2 |
39.8 .4 |
21.1 |
49.3 |
2.2 |
|
JDBM |
76.6 9.4 |
37.4 9.7 |
21.2 4.5 |
47.4 |
2.5 |
|
p value |
0.363 |
0.771 |
0.972 |
0.652 |
0.710 |
综上所述,在这项研究中,我们通过选择性激光熔化技术实现了3D打印多孔Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr支架的制备,通过体内、 外实验证实其具备良好的生物安全性与抗感染性能,为其临床转化提供依据。

来源:BioactMater生物活性材料


