您当前的位置:检测资讯 > 实验管理
嘉峪检测网 2021-03-30 14:06
近日,APIC发布了新的清洁验证指南《API工厂清洁验证指南(GUIDANCE ON ASPECTS OF CLEANINGVALIDATIONIN ACTIVEPHARMACEUTICAL INGREDIENT PLANTS)》
该指南主要涉及以下六个具体领域:
Acceptance Criteria
接受标准
Levels of Cleaning
清洁的水平
Controlof the cleaning process
清洁工艺的控制
Bracketingand Worst Case Rating
括号法和最差条件评估
Determination of the amount of residue
残留的测定
CleaningValidation Protocol
清洁验证方案
此外,还包含一系列有关清洁验证具体问题的问答。
文件目录如下:
1.0 FOREWORD
前言
2.0 OBJECTIVE
目的
3.0 SCOPE
范围
4.0 ACCEPTANCECRITERIA
接受标准
4.1 Introduction
介绍
4.2 Methods of Calculating AcceptanceCriteria
计算可接受标准的方法
4.2.1. Acceptance criteria usinghealth-based data
采用基于健康数据的可接受标准
4.2.2 Acceptance criteria using a General Limit
采用一般限度的接受标准
4.2.3. Acceptance criteria fortherapeutic macromolecules and peptides
治疗性大分子和多肽的接受标准
4.2.4 Swab Limits
擦拭法接受标准
4.2.5 Rinse Limits
淋洗法接受标准
4.2.6Rationale for the use of different limits in pharmaceutical and chemicalproduction
在制药和化学生产中使用不同限度的理由
5.0 LEVELS OFCLEANING
清洁的水平
5.1 Introduction
介绍
5.2 Cleaning Levels
清洁水平
5.3 Cleaning Verification/Validation
清洁确认/验证
6.0 CONTROLOF CLEANING PROCESS
清洁工艺的控制
7.0 BRACKETINGAND WORST CASE RATING
括号法和最差情况评估
7.1 Introduction
介绍
7.2 Bracketing Procedure
括号法程序
7.3 Cleaning Procedures
清洁程序
7.4 Investigations and Worst CaseRating
调查及最差情况评估
7.5 Worst Case Rating
最差情况评估
8.0 DETERMINATION OF THE AMOUNT OFRESIDUE
残留的测定
8.1 Introduction
介绍
8.2 Validation Requirements
验证要求
8.3 Sampling Methods
取样方法
8.4 Analytical Methods
分析方法
9.0 CLEANING VALIDATION PROTOCOL
清洁验证方案
9.1 Background
背景
9.2 Purpose
目的
9.3 Scope
范围
9.4 Responsibility
责任
9.5 Sampling Procedure
取样程序
9.6 Testing procedure
测试程序
9.7 Acceptance criteria
可接受标准
9.8 Training
培训
9.9 Deviations
偏差
9.10 Revalidation
再验证
10.0 VALIDATION QUESTIONS
验证问题
11.0 REFERENCES
参考文献
12.0 GLOSSARY
术语
13.0 COPYRIGHT AND DISCLAIMER
版权和免责声明
指南给出利用LD50数据计算PDE的原则和公式:
In orderto calculate an HBEL, the NO(A)EL or LO(A)EL should be available as POD, however,this is not always the case, certainly not for drugs in development. If thereis no NO(A)EL or LO(A)EL available, LD50 can be used as POD. However, in thiscase aconservative approach is needed and therefore moreuncertainty factors need to be applied. Other available data might also be usedin order to define an HBEL, but this is based on expert judgement. If no dataat all is available, the TTC principle according to Dolan et al. should beapplied.
为了计算HBEL, 应使用NO(A)EL或LO(A)EL作为POD(用于计算PDE或ADE)提供,然而,情况并非总是如此,对于研发中的药物肯定并非如此。如果没有NO(A)EL或LO(A)EL,可以使用LD50作为POD。然而,在这种情况下需要保守的方法,因此需要应用更多的不确定性因子。也可以使用其他可用数据来定义HBEL,但这是基于专家判断的。如果没有任何数据,则应采用Dolan等人提出的TTC原则。
Drugproducts and APIs should have at least one or several NO(A)EL or LO(A)EL valuesavailable. Only very occasionally, for example in early drug developmentstages, no NO(A)EL or LO(A)EL might be available and LD50 values can be used,but only with very conservative uncertainty factors. It is however, stronglyadvised to restrict the use of LD50 as POD in this case as LD50 values are notreliable for predicting long-term effects.
药品和原料药应至少有一个或多个NO(A)EL或LO(A)EL可用。只有在非常偶然的情况下,例如在药物开发的早期阶段,可能没有NO(A)EL或LO(A)EL,可以使用LD50值,但也需要在非常保守的不确定因子下。然而,强烈建议在这种情况下限制LD50作为POD的使用,因为LD50对预测长期影响并不可靠。
Forintermediates where limited data may be available, HBEL determination guidancewill be given by the toxicologist.
对于限度数据可用的中间体,毒理学家将给出HBEL确定的指导。
For mostsolvents and detergents HBELs are already determined and available in publicdatabases: ACGIH; OSHA; MAK; NIOSH, etc.
对于大多数溶剂和洗涤剂,HBELs已经确定并在公共数据库中可用:例如,ACGIH;OSHA;MAK;NIOSH等等。
Ingeneral, the HBEL should be determined based on following hierarchy:
一般情况下,HBEL应按照以下层次来确定:
HBELavailable (mostly for solvents and reagents): use most stringent HBEL
HBEL可用(主要为溶剂和试剂):使用最严格的HBEL
No HBEL available,but NO(A)EL or LO(A)EL available: calculate HBEL (as described) based onNO(A)EL/LO(A)EL as POD
没有HBEL可用,但有NO(A)EL或LO(A)EL:根据NO(A)EL/LO(A)EL作为POD计算HBEL(如所述)
No HBELavailable, no NO(A)EL or LO(A)EL available: use other available numerical dataas POD to determine HBEL (LD50* values, BMD)
没有HBEL 可用,没有 NO(A)EL 或LO(A)EL 可用:使用其他可用数值的数据(例如,LD50* , BMD)作为POD来确定HBEL
No HBELavailable, no other numerical toxicological data available: use other availabledata to determine HBEL (mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, CLP, etc), but this isbased on expert judgement
没有可用的HBEL,没有其他数值毒理学数据:使用其他可用数据来确定HBEL(致突变性、致癌性、CLP等),但这是基于专家判断
No data at all available: usedefault (based on QSAR) or TTC or additional testing
没有数据可用:使用默认值(基于QSAR)或TTC或额外测试
Thishierarchy should strictly be applied in setting the HBEL: the most reliablesource of data available at that moment of assessment should be used todetermine the HBEL.
在设置HBEL时,应严格应用这种层次结构:评估时应使用最可靠的数据来源来确定HBEL。
*In caseswhere no other data is available and only LD50 data is available the HBEL canbe based upon LD50 data. Calculate NOEL according to the following equation and use theresult for the establishment of HBEL
*在没有其他数据,只有LD50数据可用的情况下,HBEL可以基于LD50数据。根据下式计算NOEL,并将其用于确定HBEL:
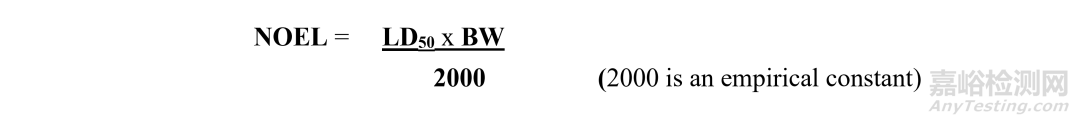

来源:GMP办公室


