您当前的位置:检测资讯 > 科研开发
嘉峪检测网 2021-04-07 14:17
本文利用海洋污物生物海鞘的被囊制备了动物纤维素水凝胶,该水凝胶具有与天然心肌组织类似的导电性和良好的力学性能。基于该水凝胶制备的心肌补片能够促进心肌细胞成熟和形成自发收缩的功能,体内移植后,该补片能提高梗死心肌的心功能。这种变废为宝的策略既能解决海洋生物污染,又能为组织工程支架材料提供再生资源。
01研究内容简介
近年来,随着海产养殖业的迅猛发展,养殖中出现的生物污染问题也日益突出。例如,在扇贝的大规模养殖过程中,常常受到海鞘等生物入侵的威胁。海鞘会黏附在扇贝及其养殖设备上进行大量的扩增,当海鞘等生物数量过多时,会与扇贝争夺养分与空间,并迅速侵占面积,取代本地物种,成为制约水产养殖业和海洋生态环境可持续发展的主要问题之一。且因大多数的海鞘没有食用价值,经常被养殖场当作废物丢弃。但是海鞘的被囊拥有丰富的纤维素成分,且该来源是目前已知的唯一的动物纤维素来源。随着近些年来不可再生资源的日益减少,纤维素等可再生的替代资源逐渐受到极大的关注,如何开发这些海鞘等污物的价值,实现废物利用,对于可持续发展来说是一件极其有意义的行为。
心血管疾病是一直导致全球人口死亡的主要原因,其中心肌梗死(MI)造成的死亡占了很大比例。但常规的治疗手段不能有效的改善心梗后瘢痕的形成,而心肌组织工程是近些年新兴的,一种具有极大应用前景的心梗治疗策略。它主要通过制备功能性仿生支架模拟天然心肌的细胞外基质,为梗死区域提供一定机械支持,修复心梗区与非心梗区的电活动,促进梗死区的血管再生,恢复心梗区的血供,以保护并提高心梗后的心功能。心肌的组织的微环境的十分复杂,对组织工程的支架材料的设计与性能都有很高的要求:1)心肌组织是一种可兴奋组织,需要良好的导电微环境为其提供电信号的传导;2)心肌组织优异的收缩舒张能力,使心脏拥有强大的泵血功能,所以支架材料需要有良好的弹性以适宜心脏的力学变化;3)众所周知,心肌组织的排列是具有一定方向性的,所以需要支架材料具有一定的方向性,能引导心肌细胞的定向排列。但是,以往报道的支架材料很少能同时满足以上条件,因此,一种与天然心肌组织相似的具有良好导电性、弹性、有序性及生物相容性的仿生支架材料是迫切需要并有待开发的。
为了解决海产养殖的生物污染问题以及制备可用于心肌修复的仿生支架材料,我们以海洋养殖废弃物为原料,对海鞘的被囊进行了升级处理,获得了天然纤维素水凝胶作为心肌修复的补片支架。海鞘被囊通过简单处理,无需化学或物理交联,就能获得具有良好导电性、弹性以及有序性的天然纤维素水凝胶,而且因为该水凝胶完全由动物纤维素构成,具有优异的生物相容性。研究证实该水凝胶在体外能促进外源性心肌细胞的成熟与功能性蛋白的表达,构建的心肌补片能实现同步性的收缩。移植到体内能促进梗死区血管的形成,移植纤维化的形成,显著提升梗死大鼠的心功能。本研究首次用海洋污物生物海鞘构建了具有天然导电性,弹性,有序性的纯动物纤维素水凝胶,并检验了该支架对心肌梗死修复的作用,初步证明了在组织工程中应用的可能性。这种变废为宝的策略为解决海洋生物污染与组织工程支架材料来源提供了思路。
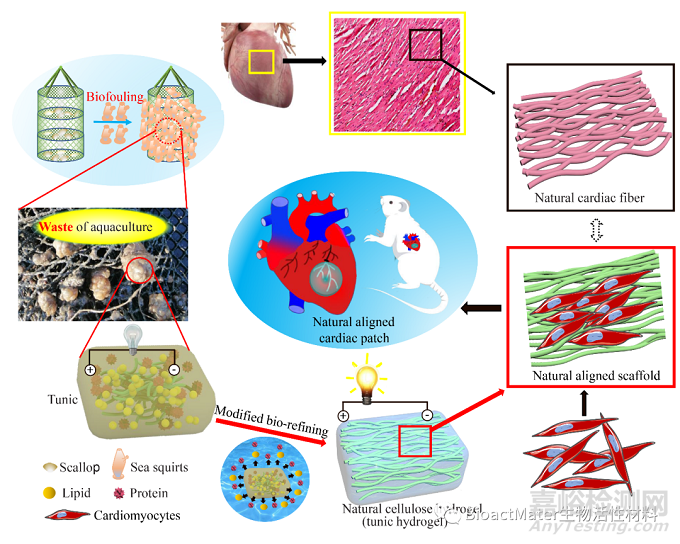
Fig. 1. The sea squirts-derived cardiac patch for myocardial infarction from waste of marine culture. The sea squirts, the waste of marine culture, could form the conductivity and well-aligned hydrogel after treating with acid and alike and significantly enhance the cardiac function of myocardial infarction rats.
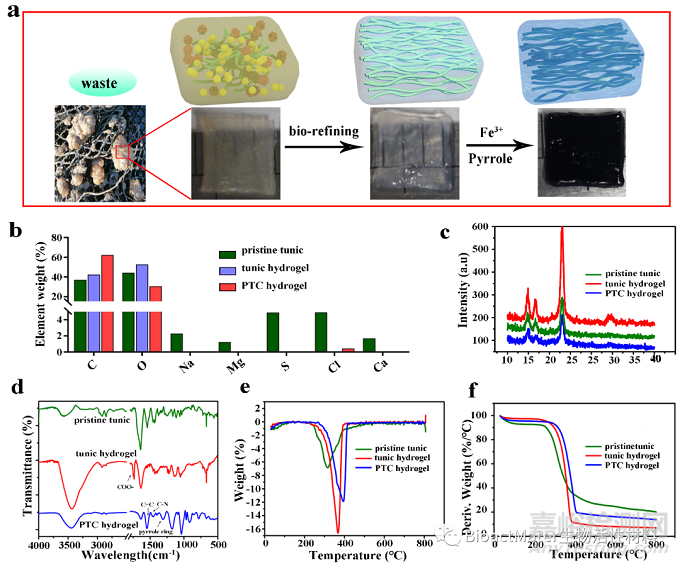
Fig. 2. The preparation of tunic cellulose hydrogel. (a) The preparation procedure of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. (b) The elemental analysis of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. (c) XRD analysis for pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. (d) FTIR spectra of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. TGA (e) and DTG (f) curves of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel.
实验结果表明,海鞘被囊作为原料构建的tunic hydrogel主要是由纤维素组成,具有良好的热稳定性 (Fig.2)。
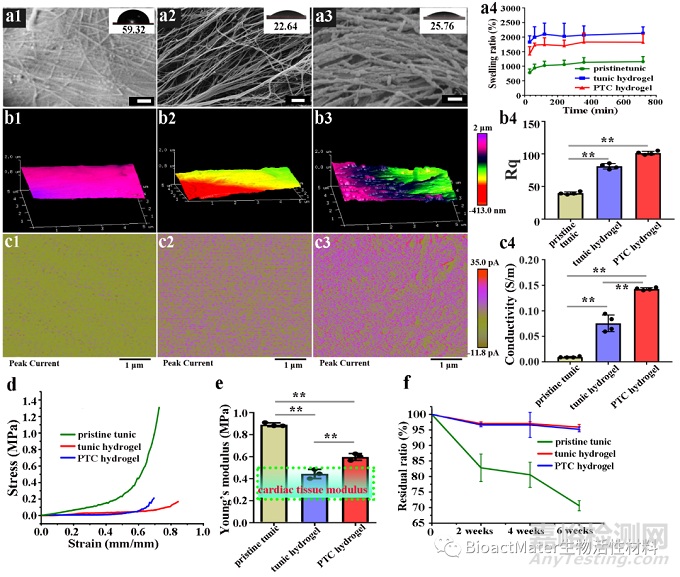
Fig. 3. The morphological, conductivity and mechanical characteristics of the scaffold. The SEM images of pristine tunic (a1), tunic hydrogel (a2) and PTC hydrogel (a3), scale bars: 200 nm. The inset are corresponding photos of contact angle on the surface of samples. (a4) The uptake water analysis of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel n=4. (b1-3) Surface morphology and (b4) corresponding surface roughness Rq of pristine tunic (b1), tunic hydrogel (b2) and PTC hydrogel (b3) revealed by AFM test. The current distribution of pristine tunic (c1), tunic hydrogel (c2) and PTC hydrogel (c3) revealed by e-AFM test, n=4. (c4) Statistical analysis of conductivity in pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel n=4. (d) The stress-strain curves of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. (e) The Young’s modulus of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel n=3. (f) The degradation ratio of pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel in physiological environment n=4. All data are presented as mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
该天然纤维素水凝胶具有良好的方向齐性,能够引导心肌细胞方向性排列。天然纤维素水凝胶(tunic hydrogel)在不负载导电纳米颗粒时就拥有与天然心肌组织类似导电性与弹性,且降解速度慢,具有长期的稳定性,可为梗死心肌提供长期的力学支撑 (Fig.3) 。
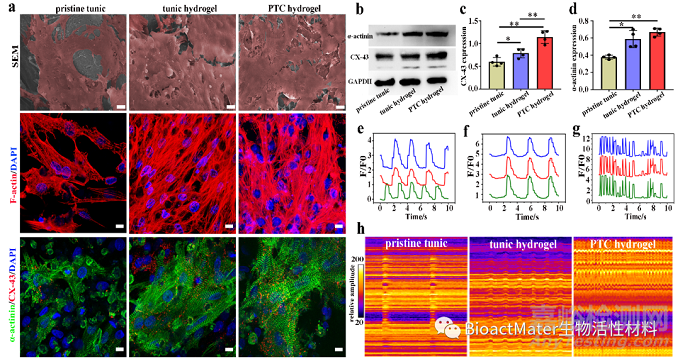
Fig. 4. The morphological and functional characteristics of cardiomyocytes in scaffolds. (a) The morphology and maturation analysis of CMs in different scaffolds at day 7 of culture. The SEM of CMs seeded on pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel, scale bars: 50 µm. The F-actin stained of cytoskeleton of CMs on pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. Expression of cardiac-specific proteins of α-actinin (green) and CX-43 (red) in the CMs on pristine tunic, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel. Scale bars: 20 µm. (b) Western blotting detection for the expressions of α-actinin protein and CX-43 protein in CMs in different scaffolds at day 7 of culture. (c-d) The quantitative proteins expression of CX-43 (c) and α-actinin (d) in CMs in different scaffolds based on western blotting detection, n=4. (e-g) Calcium transient of CMs on different scaffolds at day 7 of culture. (h) The beating behavior of the cardiomyocytes in the different scaffolds showed that more uniform contraction behavior.
在体外,该天然导电支架(tunic hydrogel)与负载了聚吡咯导电离子的高导电支架材料(PTC hydrogel)都能促进外源性心肌细胞成熟、功能化以及定向排列,但tunic hydrogel形成的心肌补片比PTC hydrogel心肌补片具有更好节律性搏动 (Fig. 4)。
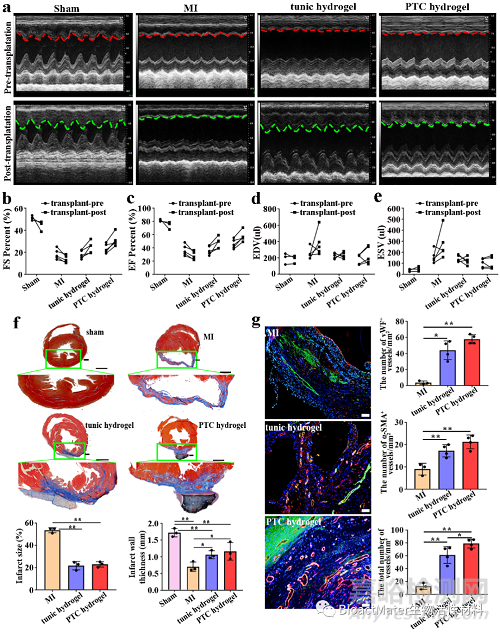
Fig. 5. Repair effect of patch in myocardial infarction rats. (a) The echocardiographic images of pretransplant (above) and posttransplant (bottom) in the sham group (control group), the MI group, tunic hydrogel and PTC hydrogel group. (b-e) Representative parameters of left ventricular function based on echocardiography of different groups after 4 weeks of implantation. (f) Masson’s staining displayed the fibrous tissue (blue) and myocardium (red) of sections of hearts from animals in different groups. Scale bars: 1 mm. Statistical analysis of infarct size and infarct wall thickness of the infarcted heart in different group (bottom), n=3. (g) vWF immunostaining (red) and α-SMA immunostaining (green) within infarcted area in different groups, n=4. Scale bars: 50 µm. The different microvessel densities within infarcted region in different groups based on vWF/α-SMA immunostaining staining. All data are presented as mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
在体内,该天然导电支架即使不负载聚吡咯导电离子(tunic hydrogel)也能达到与高导电支架材料(PTC hydrogel)类似的修复效果,且都能够为梗死区域提供一定的力学支撑,并促进梗死区血管的形成,抑制梗死区纤维化,增强心梗后的心功能。证实了从海鞘获得的天然动物纤维素支架在不进行导电修饰就可拥有良好的修复效果 (Fig. 5)。
02论文第一/通讯作者简介
共同第一作者:何玉童
博士、南方医科大学基础医学院,研究方向为天然生物材料在心肌组织工程中应用。
共同第一作者:侯鸿浩
南方医科大学基础医学院教授、博士生导师,研究方向为仿生生物材料与界面组织工程。
共同第一作者:王树启
汕头大学海洋生物研究所副教授、硕士生导师,研究方向为鱼类生理与分子生物学。
通讯作者:邱小忠
博士、南方医科大学基础医学院教授、博士生导师。主要从事生物材料、细胞与材料的相互作用、组织再生等方面的研究工作,在Advanced Functional Materials, ACS Nano, Biomaterials, Theranostics, Applied Materials Today等期刊发表论文30余篇,主持国家级及省部级项目13项。
03资助信息
上述研究工作得到了中国自然科学基金(32071363, 52003113, U1601221)广州再生医学与健康广东省实验室(2018GZR110104002)、广州市科技项目(201804020035)及广东省科技厅项目(2016B090913004)支持。
04原文信息
Yutong Hea,1, Honghao Houa,1, Shuqi Wangb,1, Rurong Lina, Leyu Wangc, Lei Yua, Xiaozhong Qiua

来源: BioactMater生物活性材料


