1、法规指南:
1.1 NMPA:(原文部分引用)
根据目前所知,亚硝胺类杂质有多种产生原因,如工艺产生、降解途径和污染引入等。具体来讲,亚硝胺类杂质可能通过以下途径引入:
(一)由工艺引入亚硝胺类杂质的风险
目前所知,NDMA、NDEA杂质可能通过亚硝化机理生成。即在一定条件下,胺类化合物尤其是仲胺,与亚硝酸钠(NaNO2)或其他亚硝化试剂反应产生亚硝胺类杂质。在同一工艺步骤中使用了能引入仲胺和亚硝化试剂的物料(包括起始物料、溶剂、试剂、催化剂、中间体等),有较高的风险引入亚硝胺类杂质;即使在不同的工艺步骤中分别使用能引入仲胺和亚硝化试剂的物料,也可能会产生亚硝胺类杂质。除物料本身带有仲胺结构外,仲胺可能的来源有:伯胺、叔胺及季铵可能引入仲胺杂质;酰胺类溶剂(如N,N-二甲基甲酰胺、N-甲基吡咯烷酮等)在适宜的条件下(如:酸性,高温等)可能产生仲胺。
亚硝化试剂可能引入来源有:亚硝酸盐、亚硝酸酯、亚硝酸、由亚硝酸盐制备的物质(如:叠氮化钠等),胺类化合物的氧化等。
(二)由污染引入的风险
原料药生产过程中使用了被亚硝胺类杂质污染的物料(起始物料、中间体、溶剂、试剂、催化剂等)可能带来亚硝胺类杂质的风险。
使用回收的物料亦有引入亚硝胺类杂质的风险。已发现的回收物料被亚硝胺污染的实例包括邻二甲苯、氯化三丁基锡(用作叠氮化三丁基锡的来源)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)。在同一生产线生产不同的品种,交叉污染也可能成为引入亚硝胺类杂质的潜在原因。
(三)降解产生风险
某些药物本身会降解产生亚硝胺类杂质,如雷尼替丁在高温下会产生亚硝胺类杂质。
1.2 EMA(17 April 2025 EMA/409815/2020 Rev.22)
Use of nitrite salts and esters (e.g. NaNO2, alkyl nitrites), or other nitrosating agents (e.g. nitroso halides, nitrosonium salts, nitrogen oxides, nitro alkanes, halogenated nitro alkanes, Fremy’s salt, nitroso sulfonamides) in the presence of secondary or tertiary amines within the same or different steps of the manufacturing process. Sources for secondary or tertiary amines can also be starting materials, intermediates, reagents, solvents (e.g. DMF, DMAc and NMP) and catalysts, which contain amine functionality, amine impurities (e.g. quaternary ammonium salts) or which are susceptible to degradation to reveal amines.
生产工艺中在二级胺或三级胺存在的相同或不同的步骤中,使用亚硝酸盐和亚硝酸酯(NaNO2,RONO)或者其他亚硝化试剂(NOCl,NO2BF4, N2O3, N2O4, MeNO2, 卤代硝基甲烷,弗氏盐,亚硝基磺酰胺)。
二级或三级胺的来源可以是含有胺官能团的,或者含有胺杂质(如季铵盐中),或者容易降解释放出胺的起始物料,中间体,试剂,溶剂(DMF,DMAc,NMP)和催化剂。
Nitrite formation by oxidation of hydroxylamine or nitrite release from nitro-aromatic precursors (e.g. by fluoro de-nitration), in the presence of secondary or tertiary amines within the same or different steps of the manufacturing process
在生产过程中,二级胺和三级胺存在的相同或不同步骤,通过羟胺氧化形成亚硝酸盐,或从硝基芳香族前体中释放亚硝酸盐(例如通过氟取代硝基过程)
Use of disinfected water (chlorination, chloro-amination, ozonisation) in the presence of secondary or tertiary amines within the same or different steps of the manufacturing process
在生产过程中,二级胺和三级胺存在的相同或不同步骤使用消毒水(氯化、氯胺化、臭氧化)
Oxidation of hydrazines, hydrazides and hydrazones by hypochlorite, air, oxygen, ozone and peroxides in the manufacturing process or during storage.
在生产过程中或储存期间,肼类、酰肼类和腙类化合物被次氯酸盐、空气、氧气、臭氧及过氧化物氧化的情况
Use of contaminated raw, recovered or recycled materials (e.g. solvents, reagents and catalysts) in the API manufacturing process.在原料药生产过程中使用受污染的原始、回收或再生材料(例如溶剂、试剂和催化剂)Use of contaminated starting materials and intermediates supplied by vendors who use processes or raw materials which may contain residual nitrosamines or nitrosating agents
使用受污染的起始物料和中间体,这些物料由供应商提供,而供应商所采用的工艺或原材料可能含有残留的亚硝胺或亚硝化试剂。
Carry-over of nitrosamines deliberately generated (e.g. as starting materials or intermediates) during the manufacturing process
在生产过程中故意生成的亚硝胺(例如,作为起始原料或中间体)的残留。
Cross-contamination due to different processes being run successively on the same manufacturing line在相同的生产线上运行不同的工艺导致的交叉污染。
Carry-over of impurities between process steps due to operator-related errors or insufficiently detailed batch records such as inadequate phase separations during work-up procedures.
由于操作员相关错误或批次记录不够详细(例如在处理过程中相分离不充分),导致杂质在各工艺步骤之间残留。
Use of contaminated recovered or recycled materials (e.g. solvents, reagents and catalysts) where the recovery is outsourced to third parties who are not aware of the content of the materials they are processing. Recovery processes carried out in non-dedicated equipment should also be considered.
使用受污染的回收材料(例如溶剂、试剂和催化剂),而这些材料的回收工作外包给了第三方,而第三方并不清楚他们所处理材料的成分。在非专用设备中进行的回收过程也应予以考虑。
1.3 FDA(Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs Guidance for Industry. September 2024,R2)
Formation of nitrosamines is possible in the presence of secondary, tertiary, or quaternary amines20 and nitrite salts21 under acidic reaction conditions. Under these conditions, nitrite salts may form nitrous acid, which can react with an amine to form a nitrosamine.
在酸性反应条件下,若存在仲胺、叔胺或季胺以及亚硝酸盐,就有可能形成亚硝胺。在这些条件下,亚硝酸盐可能会生成亚硝酸,而亚硝酸可与胺发生反应形成亚硝胺。
There is a greater risk of nitrosamine formation if nitrous acid is used to quench residual azide (a reagent commonly used in tetrazole ring formation or introduction of azide functional group into a molecule) in the presence of precursor amines.
在胺前体存在下,如果用亚硝酸淬灭残留叠氮(一种用于四氮唑环合成或者分子中引入叠氮官能团的试剂)会有更大的风险形成亚硝胺。
Nitrites used as reagents in one step can carry over into subsequent steps, despite purification operations, and react with amines to generate nitrosamine impurities. Therefore, whenever nitrite salts are present, carryover into subsequent steps cannot be ruled out. In general, processes that use nitrites in the presence of secondary, tertiary, or quaternary amines are at risk of generating nitrosamine impurities.
一步反应中用作试剂的亚硝酸盐,尽管经过纯化操作,仍可能带入后续步骤,并与胺类反应生成亚硝胺杂质。因此,只要存在亚硝酸盐,就不能排除其带入后续步骤的可能性。一般来说,在仲胺、叔胺或季胺存在的情况下使用亚硝酸盐的工艺,存在生成亚硝胺杂质的风险。
Amines may be present in a manufacturing process for a variety of reasons. The API (or API degradants), intermediates, or API raw materials22 may contain secondary or tertiary amine functional groups. Tertiary and quaternary amines may also be added intentionally as reagents or catalysts. All of these types of amines can react with nitrous acid or other nitrosating agents to form nitrosamines
在制造过程中,胺类物质的存在可能有多种原因。原料药(或原料药降解产物)、中间体或原料药原料可能含有仲胺或叔胺官能团。叔胺和季胺也可能被有意添加作为试剂或催化剂。所有这些类型的胺都能与亚硝酸或其他亚硝化剂反应生成亚硝胺。
Amide solvents, which are susceptible to degradation under certain reaction conditions, are another source of secondary amines.
酰胺溶剂,在特定反应条件下,易发生降解,是二级胺的另一来源
Secondary amines could also be present as impurities in amide solvents. For example, dimethylamine, which can react with nitrous acid to form NDMA, may exist as an impurity in N,N-dimethylformamide.
二级胺可能作为杂质在酰胺溶剂中存在,如DMF中的二甲胺。
Tertiary and quaternary amines used as reagents in the synthesis of APIs may contain other amine impurities. Tertiary amines, such as triethylamine, have been shown to contain low levels of other secondary amines (such as dipropylamine and isopropylethylamine). Secondary and tertiary amines may be present as impurities or degradants formed by dealkylation of quaternary amines. For example, a common phase-transfer catalyst, tetrabutylammonium bromide, may contain tributyl- and dibutylamine impurities. The amine impurity level that may lead to nitrosamine impurities in the API is process-dependent and should be determined by each API manufacturer.
在原料药合成中用作试剂的叔胺和季胺可能含有其他胺类杂质。叔胺(如三乙胺)已被证实含有少量其他仲胺(如二丙胺和异丙基乙胺)。仲胺和叔胺可能作为杂质存在,也可能是季胺脱烷基化形成的降解产物。例如,一种常见的相转移催化剂-四丁基溴化铵,可能含有三丁胺和二丁胺杂质。可能导致原料药中产生亚硝胺杂质的胺类杂质水平取决于工艺,应由各原料药生产商确定。
Vendor-Sourced Raw Materials Containing Nitrosamine Impurities
来源于供应商的原料含有亚硝胺杂质:
Nitrosamines have been found in fresh solvents (ortho-xylene, toluene, and methylene chloride) when impurities were carried over during transfer between storage vessels used in the shipment of solvents.
在用于溶剂运输的储存容器之间转移溶剂时,若杂质被带入,新鲜溶剂(邻二甲苯、甲苯和二氯甲烷)中就会发现亚硝胺。
Sodium nitrite is a known impurity in some starting materials (such as sodium azide) and may be present and react with amines under acidic conditions to form nitrosamines. Nitrate-containing raw materials, such as potassium nitrate, may contain nitrite impurities. The amount of nitrite impurity that can be tolerated is process-dependent and should be determined by each API manufacturer.
亚硝酸钠是某些起始原料(如叠氮化钠)中已知的杂质,在酸性条件下可能存在并与胺类反应生成亚硝胺。含硝酸盐的原料(如硝酸钾)可能含有亚硝酸盐杂质。可耐受的亚硝酸盐杂质含量取决于工艺,应由各原料药生产商确定。
Secondary or tertiary amines have been reported as impurities in some raw materials (see details in section III.B.2.) and in fresh solvents such as toluene.
据报道,仲胺或叔胺在一些原材料中(详见第 III.B.2 节)以及甲苯等新鲜溶剂中会作为杂质存在。
API starting materials and API intermediates may be at risk through cross-contamination at the manufacturing site if these materials are manufactured where nitrosamine impurities can carry over from other processes.
如果原料药起始物料和原料药中间体是在可能从其他工艺中带入亚硝胺杂质的场所生产的,那么在生产现场,这些物料可能会面临交叉污染的风险。
Recovered Solvents, Reagents, and Catalysts as Sources of Nitrosamine Impurities回收溶剂,试剂,催化剂的使用是亚硝胺杂质的潜在来源。
Recovered materials such as solvents, reagents, and catalysts may pose a risk of nitrosamine impurities due to the presence of residual amines (such as trimethylamine or diisopropylethylamine). If the recovery process involves a quenching step (i.e., nitrous acid used to decompose residual azide), nitrosamines could form during solvent recovery. These nitrosamines may be entrained if they have boiling points or solubility properties similar to the recovered materials, depending on how recovery and subsequent purification takes place (e.g., aqueous washes or distillation). This further increases the risk of nitrosamines in material recovery. For 8 Contains Nonbinding Recommendations these reasons, some drug products using APIs manufactured by certain “low” risk processes23 were found to contain nitrosamine impurities. The Agency has observed the following due to this root cause:
回收的材料(如溶剂、试剂和催化剂)可能因存在残留胺(如三甲胺或二异丙基乙胺)而有亚硝胺杂质风险。如果回收过程包含淬灭步骤(即使用亚硝酸分解残留的叠氮化物),那么在溶剂回收过程中可能会形成亚硝胺。如果这些亚硝胺的沸点或溶解度特性与回收材料相似,它们可能会被夹带,这取决于回收及后续纯化的方式(例如水洗或蒸馏)。这进一步增加了材料回收过程中出现亚硝胺的风险。出于这些原因,一些使用通过某些“低” 风险工艺生产的原料药的药品被发现含有亚硝胺杂质。基于这一根源,该机构观察到以下情况:
• A manufacturing site may produce the same API by more than one synthetic process that uses common solvents. If any of those synthetic processes produces nitrosamines or contains precursor amines, the solvents sent for recovery are at risk. The use of recovered solvents that are commingled from different processes or across manufacturing lines without control and monitoring can introduce nitrosamine impurities. If a recovered solvent with nitrosamine impurities is used to manufacture an API, the API will contain the impurities even if the synthetic route is not normally susceptible to nitrosamine formation.
一个生产场地可能通过多种使用通用溶剂的合成工艺生产同一种原料药。如果这些合成工艺中的任何一种会产生亚硝胺或含有前体胺,那么送去回收的溶剂就会面临风险。在没有控制和监测的情况下,使用从不同工艺或不同生产线混合回收的溶剂,可能会引入亚硝胺杂质。如果使用含有亚硝胺杂质的回收溶剂来生产原料药,那么即使该合成路线通常不易形成亚硝胺,原料药中也会含有这些杂质。
• Recovery of raw materials (e.g., solvents, reagents, and catalysts) is often outsourced to third-party contractors. Process outsourcing can pose a risk if the third-party recovery facility does not receive enough specific information on the contents of the materials it is processing and relies solely on routine recovery processes.
原材料(例如溶剂、试剂和催化剂)的回收工作通常外包给第三方承包商。如果第三方回收设施没有收到关于其处理的材料成分的足够具体信息,而仅依赖常规回收流程,那么流程外包就可能带来风险。
• Raw materials can contain nitrosamine impurities if adequate cleaning of equipment between customers, or between different materials, is not carried out or is not validated as capable of removing each impurity of concern. It was reported that nitrosamine impurities were introduced into recycled ortho-xylene and toluene due to inadequate cleaning and use of shared storage equipment between different customers. Inadequate and unvalidated cleaning procedures can also lead to cross-contamination if precautions to avoid nitrosamines are not in place before materials from different customers are combined for recovery. For example, nitrosamine impurities were introduced into lots of the catalyst tri N-butyltin chloride (used as a source of tri-N-butyltin azide) at a third-party contractor facility due to the combining of catalyst lots from multiple customers.
如果在客户之间、不同物料之间对设备的清洁不充分,或者未验证清洁是否能够去除每种相关杂质,那么原材料可能会含有亚硝胺类杂质。据报道,由于清洁不充分以及不同客户共用存储设备,亚硝胺类杂质被引入到回收的邻二甲苯和甲苯中。如果在将不同客户的物料合并回收之前,没有采取避免亚硝胺产生的预防措施,那么不充分且未经验证的清洁程序也可能导致交叉污染。例如,在一家第三方承包商的工厂里,由于将多个客户的催化剂批次进行合并,亚硝胺类杂质被引入到数批三正丁基氯化锡催化剂(用作三正丁基叠氮化锡的来源)中。
Quenching Process as a Source of Nitrosamine Impurities
淬灭工艺-亚硝胺的来源
There is a risk of nitrosamine formation when a quenching step is conducted directly in the main reaction mixture (i.e., when nitrous acid is added to the reaction mixture to decompose residual azide). This allows nitrous acid to come into direct contact with residual amines in the raw materials used in the manufacturing process. The nitrosamine impurities could be carried to the subsequent steps if adequate removal or purification operations are not in place, or if the operations are not optimized for removing specific impurities of concern. These impurities can enter the downstream process once they are introduced. Even if the quenching process is conducted outside of the main reaction mixture , there is a risk if recovered materials containing nitrosamine impurities are introduced into the main process.
当淬灭步骤直接在主反应混合物中进行时(即向反应混合物中加入亚硝酸以分解残留的叠氮化物时),存在亚硝胺形成的风险。这会使亚硝酸与制造过程中使用的原材料中的残留胺直接接触。如果没有适当的去除或纯化操作,或者这些操作未针对去除特定的目标杂质进行优化,亚硝胺杂质可能会被带入后续步骤。这些杂质一旦引入,就会进入下游工艺。即使淬灭过程在主反应混合物之外进行,如果将含有亚硝胺杂质的回收物料引入主工艺,也会存在风险。
Lack of Process Optimization and Control缺少工艺优化和控制Another potential source of formation of nitrosamine impurities is lack of optimization of the manufacturing process for APIs when reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, or the sequence of adding reagents, intermediates, or solvents are inappropriate or poorly controlled. FDA has seen instances in which reaction conditions varied widely between batches and even between different processing equipment in the same facility for the same API. Additionally, certain manufacturing processes using forced air, such as fluid bed drying at elevated temperature and jet milling, can create favorable conditions for nitrosamine formation in at-risk APIs when nitrogen oxides in the air react with the APIs. The multiple root causes of nitrosamine impurities listed above can occur within the same API process. Therefore, multiple strategies may be necessary to identify all potential sources of nitrosamine formation. Typical routine tests (e.g., high performance liquid chromatography) for API purity, identity, and known impurities are unlikely to detect the presence of nitrosamine impurities. Further, each failure mode could result in different nitrosamines in different amounts across batches from the same process and the same API manufacturer, with nitrosamine impurities detected in some batches but not all.
亚硝胺杂质形成的另一个潜在来源是原料药生产工艺缺乏优化,例如温度、pH 值或加入试剂、中间体、溶剂的顺序等反应条件不合适或控制不当。美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)已发现,对于同一种原料药不同批次之间,甚至同一设施中不同加工设备之间的反应条件差异很大的情况。此外,某些使用压缩空气的生产工艺,如高温流化床干燥和气流粉碎,当空气中的氮氧化物与原料药发生反应时,可能会为存在风险的原料药中形成亚硝胺创造有利条件。上述列出的亚硝胺杂质的多种根本原因可能在同一原料药工艺中出现。因此,可能需要多种策略来识别亚硝胺形成的所有潜在来源。用于检测原料药纯度、鉴别以及已知杂质的典型常规测试(例如高效液相色谱法)不太可能检测出亚硝胺杂质的存在。此外,每种失效模式都可能导致同一工艺和同一原料药生产商生产的不同批次中出现不同种类和不同含量的亚硝胺,有些批次中检测出亚硝胺杂质,而有些批次则未检测出。
2、技术文献
Regulatory Experiences with Root Causes and Risk Factors for Nitrosamine Impurities in Pharmaceuticals
该文章由加拿大卫生部,美国FDA,新加坡卫生科学局,巴西国家卫生监督局,EMA阿姆斯特丹,德国联邦药品与医疗器械研究所工作人员联合发表。
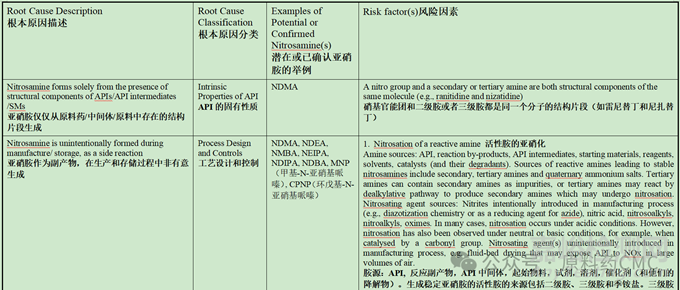
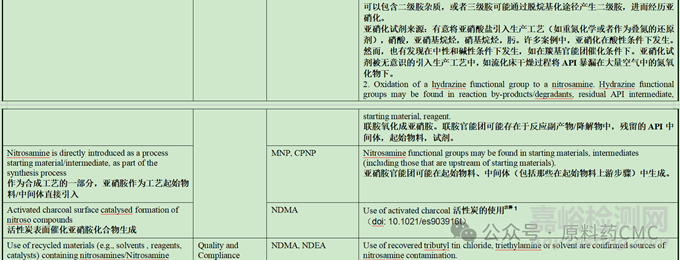
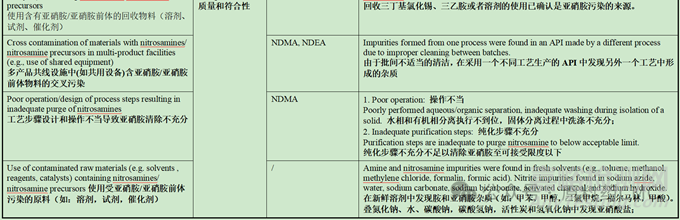
Root Causes and Risk Factors from Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
原料药中形成亚硝胺的根本原因和风险因素
注释1:研究表明:活性炭可以在水中催化亚硝酸盐和二甲胺形成亚硝胺。但当水中亚硝酸盐的含量低于0.023mg/L时,则不存在该风险。另外,该研究结果给出,水溶液中生成亚硝胺的量占总体的10%,90%的亚硝胺是在后续干燥过程中产生。反应条件研究结果表明,在活性炭催化的亚硝胺形成过程中,仲胺是亚硝胺的前体,且胺的浓度和结构对反应有显著影响。(与其疏水性可能相关,更容易被富集到活性炭上,浓度提高)。随着pH值的升高亚硝胺的生成量增加,与亚硝胺在酸性条件下的反应条件相悖,可能存在其他因素,最终推测在氧气的存在下,活性炭表面能够催化氧化吸附的仲胺和亚硝酸盐形成亚硝胺。
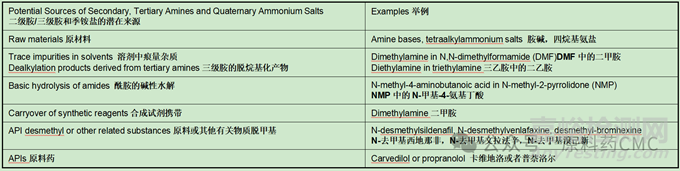
Examples of nitrosamine precursors - amines.亚硝胺前体-胺
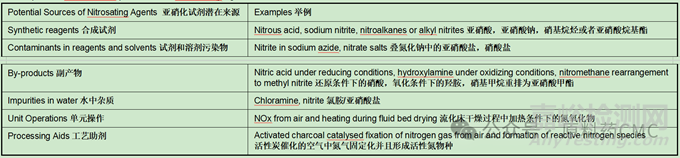
Examples of nitrosamine precursors - nitrosating agents.亚硝胺前体-亚硝化试剂
3、参考文献
Regulatory Experiences with Root Causes and Risk Factors for Nitrosamine Impurities in Pharmaceuticals.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2022.12.022