近日,FDA发布了PROGRAM 7356.002F《API 检查指南》,文件为 API 生产工厂提供全面的 CGMP 检查范围,并于2025年9月2日实施。
文件包含以下内容:
PART I – BACKGROUND
第一部分
背景
1. Introduction
介绍
2. Applicable Statute, Regulations, and Guidances
适用法律、法规和指南
3. Scope of APIs Covered by This Program
本程序涵盖的 API 范围
4. Definitions
定义
PART II –IMPLEMENTATION
第二部分
实施
1. Objective
目的
2. Program Management Instructions
程序管理说明
A. Selecting Sites
场地选择
B. Selecting Investigators
检查员的选择
C. Selecting Inspection Types
检查类型的选择
D. Selecting Systems
被检查系统的选择
E. Selecting APIs
API选择
F. Selecting Profile Classes
配制文件类型选择
PART III –INSPECTIONAL
第三部分 检查
1. Operations
操作
A. Inspection Approaches
检查方法
B. System Coverage
被检查系统的覆盖范围
C. Preparing the Inspection Strategy
准备检查策略
2. Reporting
报告
A. Special Instructions for Responding to a Form
FDA 483回复 FDA 483 的特别说明
PART IV –ANALYTICAL
第四部分 分析
PART V –REGULATORY/ADMINISTRATIVE STRATEGY
第五部分 监管/行政策略
PART VI –REFERENCES, ATTACHMENTS, AND PROGRAM CONTACTS
第六部分 参考文献、附录和程序联系方式
1. References
参考文献
2. Attachments– None
附录 无
3. Program Contacts
程序联系方式
A. CDER
B. OII
文件详细介绍了质量体系、设施与设备系统、生产系统、物料系统、包装与标签系统和实验室控制系统的检查内容:
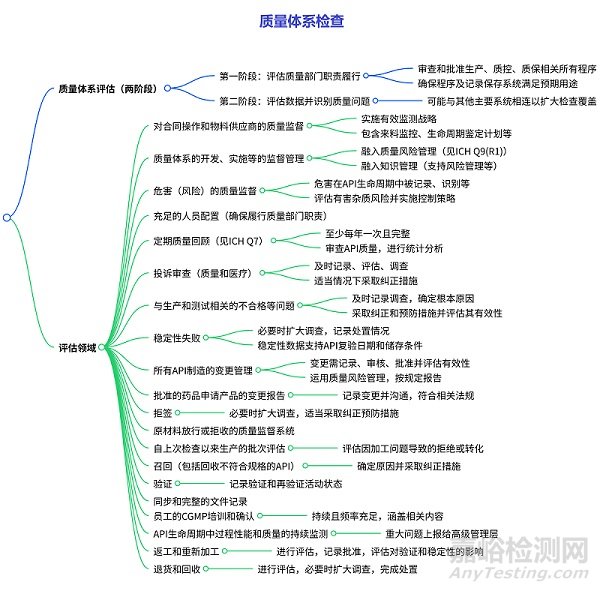
质量系统的检查
分为两个阶段:
第一阶段:调查人员评估质量部门是否履行了审查和批准与生产、质量控制和质量保证相关的所有程序的责任,同时评估质量部门是否确保这些程序及相关记录保存系统足以满足预期用途。
第二阶段:调查人员对数据进行评估,识别任何质量问题,且该阶段可能与其他主要系统相连以扩大检查覆盖范围。
涵盖多个方面,包括对合同操作和物料供应商的质量监督(需实施有效监测战略等);质量体系开发、实施等的监督管理(融入质量风险管理和知识管理);危害(如交叉污染、有害杂质)的质量监督(在 API 生命周期中进行记录、评估等);充足的人员配置;定期质量回顾(至少每年一次,含 API 质量审查和统计分析);投诉审查(及时记录、调查等);生产和测试相关的不合格等问题的处理(及时调查、采取纠正预防措施);稳定性失败的应对(扩大调查、记录处置等);API 制造的变更管理(记录、审核、评估风险等);批准药品的变更报告(符合法规);拒签、原材料放行 / 拒收的质量监督;自上次检查以来生产批次的评估;召回(确定原因、采取纠正措施);验证(记录相关活动状态);同步完整的文件记录;员工 CGMP 培训(持续且涵盖相关内容);API 生命周期中过程性能和质量的监测(重大问题上报);返工和重新加工(评估、记录等);退货和回收(评估、调查等)。同时,文件多次引用 ICH 相关指南及 FDA 法规作为参考依据。
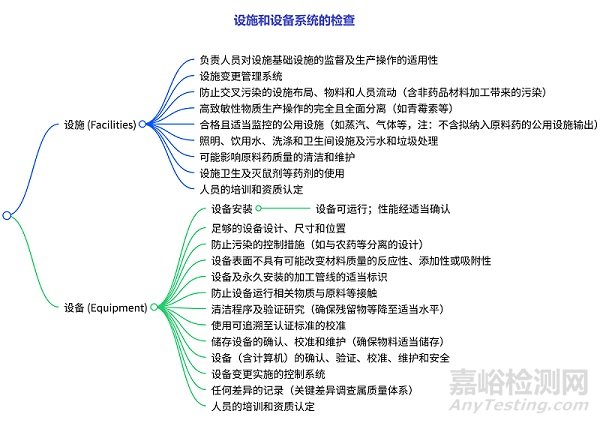
设施和设备系统的检查
设施检查:涉及人员监督、变更管理、布局与防污染、高致敏性物质生产隔离、公用设施监控、基础设施(照明、水系统等)、清洁维护、卫生与药剂使用、人员培训等。设备检查:包括安装与性能、设计尺寸位置、防污染控制、表面特性、标识、防物质接触、清洁验证、校准标准、储存设备维护、设备全流程管理(含计算机)、变更控制、差异记录、人员培训等。
物料系统的检查
涵盖人员培训与资质、物料及容器的标识、储存、隔离与先进先出使用,代表性样品采集与检验,关键物料供应商审计监控,不合格物料处理,工艺用水和气体系统适用性,计算机化流程的确认验证与安全,物料处理变更管理,批次分发及差异记录,以及起始物料等的风险管理计划等内容的检查。
生产系统的检查
包含人员培训、生产程序管理、关键活动控制、偏差处理、产量监控、工艺验证、API 安全控制、生产时限、设备标识、规格合理性、过程控制与检测、物料回收、交叉污染防控、自动化流程验证、统计评估、变更管理、批记录管理及有害杂质风险控制等的检查,详细列出了需要评估的内容及相关要求。
包装和标签系统的检查
包含人员培训资质、物料验收、程序制定与执行、变更管理、标签储存与控制、记录管理、成品检查、有效期标注、操作验证、差异记录及重新包装要求等多个方面的检查。
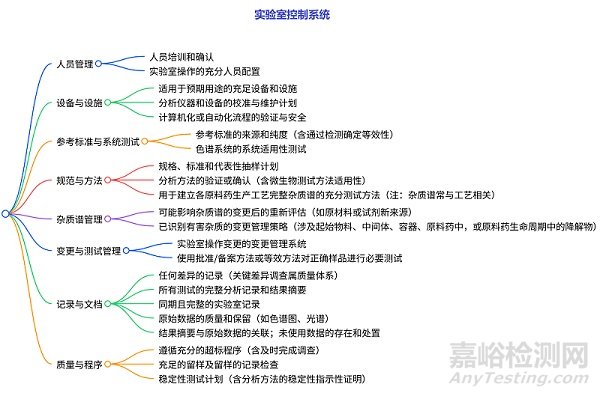
实验室控制系统的检查
包含人员管理、设备与设施(配置、校准维护、自动化流程安全)、参考标准与系统测试(来源纯度、色谱系统适用性)、规范与方法(抽样计划、方法验证、杂质谱测试)、杂质谱管理(变更后重评估、有害杂质变更策略)、变更与测试管理(操作变更系统、样品测试要求)、记录与文件(差异记录、分析记录等)、质量与程序(超标处理、留样、稳定性测试)等多方面的检查,明确了需要评估的内容及相关要点。
翻译如下:
Active Pharmaceutical ingredient Process InspectionAPI
工艺检查
PART I – BACKGROUND
第一部分 -背景
1. Introduction
引言
This compliance program applies a risk-based inspection strategy for surveillance inspections of API manufacturing facilities. The procedures in this compliance program maximize the use of history associated with a particular firm’s operations. These risks can include the firm’s compliance resources, the technology employed, the purported characteristics of the API, and the intended use of the API in the drug product, if known. This compliance program also provides procedures for coverage of for-cause inspections.
本合规计划对活性药物成分(API)生产设施的监督检查采用基于风险的检查策略。本合规计划中的程序最大程度利用与某一特定公司运营相关的历史情况。这些风险可包括公司的合规资源、所采用的技术、API 宣称的特性,以及(若已知)API 在药品中的预期用途。本合规计划还规定了有因检查的覆盖程序。
An API is:
活性药物成分(API)是:
[Any component that is intended to furnish pharmacological activity or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease, or to affect the structure or any function of the body of man or other animals. The term includes those components that may undergo chemical change in the manufacture of the drug product and be present in the drug product in modified form intended to furnish the specified activity or effect.]
[旨在在疾病的诊断、治愈、减轻、治疗或预防中提供药理活性或其他直接作用,或影响人类或其他动物身体的结构或任何功能的任何成分。该术语包括那些在药品生产过程中可能发生化学变化,并以旨在提供特定活性或作用的修饰形式存在于药品中的成分。]
API production processes commonly include a series of operations. Major operations or steps in an API production process may include multiple chemical synthesis and fermentation, purification, crystallization, drying, milling, packing, labeling, and testing. This compliance program applies to all API manufacturing operations at the establishment, including receipt of materials, production, packaging, repackaging, labeling, relabeling, quality control, release, contract testing, storage and distribution of APIs, and related controls.
API 生产流程通常包括一系列操作。API 生产流程中的主要操作或步骤可能包括多重化学合成与发酵、纯化、结晶、干燥、研磨、包装、贴标和测试。本合规计划适用于机构内的所有 API 生产操作,包括物料接收、生产、包装、重新包装、贴标、重新贴标、质量控制、放行、合同测试、API 的储存和分销,以及相关控制。
2. Applicable Statute, Regulations, and Guidances
适用的法规、规章和指南
Under section 510 of the FD&C Act,⁶ API manufacturers must register their establishments with FDA and list their APIs in commercial distribution unless exempted under 21 CFR 207.13. Foreign drug manufacturers are also required to register their establishments and list all drugs imported or offered for import into the United States. Refer to 21 CFR 207.25 (h) for additional information on establishment registration requirements for foreign drug establishments.
根据《联邦食品、药品和化妆品法案》(FD&C 法案)第 510 条,⁶API 制造商必须向 FDA 注册其机构,并列出其商业分销中的 API,除非符合 21 CFR 207.13 的豁免规定。外国药品制造商也必须注册其机构,并列出所有进口到或拟进口到美国的药品。有关外国药品机构的注册要求,可参考 21 CFR 207.25 (h) 获取更多信息。
APIs are subject to the adulteration provisions of section 501 (a)(2)(B) of the FD&C Act, which requires that all drugs are manufactured in conformance with CGMP requirements. No distinction is made between an API and a drug product in the FD&C Act, and if either fails to comply with CGMP requirements for the product, FDA has no published compliance policy specifying a requirement for APIs or drug products. Thus, the CGMP requirements in CGMP regulations are frequently cited in the FD&C Act rather than the requirements for drug products in parts 210 and 211 (21 CFR parts 210 and 211).
API 受《联邦食品、药品和化妆品法案》第 501 (a)(2)(B) 条有关掺假规定的约束,该条要求所有药品的生产符合现行良好生产规范(CGMP)要求。《联邦食品、药品和化妆品法案》中并未对 API 和药品制剂加以区分,且若其中任何一种未符合产品的 CGMP 要求,FDA 尚未发布明确针对 API 或药品制剂的合规政策。因此,《联邦食品、药品和化妆品法案》中经常引用 CGMP 法规中的 CGMP 要求,而非第 210 和 211 部分(21 CFR 第 210 和 211 部分)中针对药品制剂的要求。
FDA has long recognized that the concepts in the CGMP requirements for drug products in parts 210 and 211 are valid and applicable for API manufacturing. These concepts include: (1) ensuring drug quality by using suitable equipment and employing appropriately qualified and trained personnel; (2) establishing adequate written procedures and controls designed to ensure that manufacturing processes and controls are valid; (3) establishing a system of tests for in-process materials and drug products; and (4) ensuring that drug products are stable for their intended period of use.
FDA 长期认可 21 CFR 第 210 和 211 部分中成品药的 CGMP 理念适用于 API 生产,包括:(1)通过使用适宜设备和资质合格的人员确保药品质量;(2)制定充分的书面程序和控制措施以保证生产过程及控制有效;(3)建立中间物料和成品药的检测体系;(4)确保药品在预期使用期限内稳定。
FDA expects API manufacturers to: (1) apply CGMP to the API production process beginning with the use of starting materials; and (2) validate critical process steps that affect the quality and purity of the final API. The appropriate level of control is highly dependent on the manufacturing process and increases throughout the process as it proceeds from early steps to final isolation and purification steps. The appropriate level of control depends on the risk or criticality associated with each specific process step.FDA 要求 API 制造商:(1)从起始物料使用阶段即对 API 生产过程实施 CGMP;(2)验证影响最终 API质量和纯度的关键工艺步骤。控制水平取决于生产工艺,且随流程从早期步骤推进至最终分离纯化步骤而逐步提高,具体取决于各步骤的风险或关键程度。
In 2001, FDA published the ICH guidance for industry Q7 Good Manufacturing Practice Guidance for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. ICH Q7 represents FDA’s current thinking on CGMP for APIs. Thus, API and related manufacturing and testing facilities that follow this guidance will generally be considered in compliance with the statutory CGMP requirement. However, alternative approaches may be used if such approaches satisfy the requirements of section 501(a)(2)(B) of the FD&C Act and ensure that the API meets its purported purity, identity, and quality characteristics.
FDA 于 2001 年发布 ICH 行业指南 Q7《活性药物成分良好生产规范》。ICH Q7 代表 FDA 对 API 的CGMP 现行观点,因此遵循该指南的 API 生产及检测设施通常被视为符合法定 CGMP 要求。但若替代方法能满足《FD&C 法案》第 501 (a)(2)(B) 条并确保 API 符合其声称的纯度、标识及质量特性,亦可采用。
ICH Q7 provides guidance to industry on the extent and application of CGMP for manufacturing APIs under an appropriate quality system. The recommendations in ICH Q7 are also intended to help ensure that APIs meet the quality and purity characteristics that they purport or are represented to possess. Investigators should use ICH Q7 as a guideline for inspecting API manufacturers and related facilities.
ICH Q7 为行业提供在适宜质量体系下 API 生产的 CGMP 范围及应用指南,其建议旨在确保 API 符合声称的质量和纯度特性。检查人员应将 ICH Q7 作为检查 API 制造商及相关设施的指导文件。
As part of FDA’s continued efforts to advance the Pharmaceutical Quality for the 21st Century initiative, FDA is pursuing strategies to ensure the implementation of an effective pharmaceutical quality system as described in the ICH guidance for industry Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System (April 2009). In addition, FDA published the ICH guidance for industry Q9(R1) Quality Risk Management (May 2023) to provide principles and examples of tools for quality risk management that can be applied to different aspects throughout a product's lifecycle to ensure pharmaceutical quality. To facilitate the management of postapproval chemistry, manufacturing, and controls changes in a more predictable and efficient manner, FDA published the ICH guidance for industry Q12 Technical and Regulatory Considerations for Pharmaceutical Product Lifecycle Management and its Annexes (May 2021) and the draft guidance for industry ICH Q12: Implementation Considerations for FDA-Regulated Products (May 2021). Knowledge management, change management, and quality risk management principles should be applied to API manufacturing operations holistically to help ensure API quality. These principles are described in the guidance for industry Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical CGMP Regulations (September 2006) in addition to ICH Q9(R1), Q10, and Q12.
作为 “21 世纪药品质量” 倡议的持续努力,FDA 致力于推动实施 ICH Q10《药品质量体系》(2009 年4月)所述的有效药品质量体系。此外,FDA 发布 ICH Q9 (R1)《质量风险管理》(2023年5月),提供全产品生命周期内可应用于各环节的质量风险管理原则及工具示例;为促进上市后化学、生产和控制变更的可预测性和高效管理,发布 ICH Q12《药品生命周期管理的技术和监管考量》及其附件(2021年 5月)和草案《ICH Q12:FDA 监管产品的实施考量》(2021年5月)。知识管理、变更管理和质量风险管理原则应全面应用于 API 生产,以确保质量。这些原则详见《药品 CGMP 的质量体系方法》(2006年9月)及 ICH Q9 (R1)、Q10、Q12。
To enhance FDA’s regulation of API manufacturing and quality, FDA may use additional information sources to inform its regulatory oversight. This may include the following: (1) other inspections conducted by FDA (e.g., preapproval and postapproval inspections); (2) existing inspection reports requested from trusted foreign regulatory partners through mutual recognition agreements and other confidentiality agreements; and (3) remote regulatory assessments,including (a) records or other information requested directly from facilities and other inspected entities under section 704(a)(4) of the FD&C Act and (b) remote interactive evaluations conducted where appropriate.
为加强 API 生产和质量监管,FDA 可利用其他信息来源辅助监管,包括:(1)FDA 开展的其他检查(如批准前和批准后检查);(2)通过互认协议及其他保密协议从可信外国监管机构获取的现有检查报告;(3)远程监管评估,包括(a)根据《FD&C 法案》第 704 (a)(4) 条直接向设施及其他被检查实体索取的记录或信息,(b)在适当情况下进行的远程互动评估。
3. Scope of APIs Covered by This Program
本程序涵盖的 API 范围
This compliance program applies to the manufacture of APIs for use in human drug products, including:
本程序适用于人用药品 API 的生产,包括:
Small molecule APIs and critical intermediates manufactured by chemical synthesis
化学合成的小分子 API 及关键中间体
Polypeptides consisting of up to 40 amino acids that are manufactured by chemical synthesis or fermentation
化学合成或发酵生产的含至多 40 个氨基酸的多肽
Antibiotics and other small molecule APIs produced by microbial fermentation
微生物发酵生产的抗生素及其他小分子API
This compliance program does not cover APIs for blood, vaccines, allergenics, tissues, and cellular and gene therapies. These products are regulated by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. CGMP inspections of APIs that are proteins are conducted using compliance program 7356.002M-Surveillance Inspections of Protein Drug Substance Manufacturers. Examples of biological products that contain APIs that are proteins include, but are not limited to:
本程序不涵盖血液、疫苗、变应原、组织及细胞和基因治疗用 API,此类产品由生物制品评价与研究中心监管。蛋白质类 API 的 CGMP 检查遵循合规程序 7356.002M 《蛋白质活性药物成分制造商的监督检查》。含蛋白质类 API 的生物制品示例包括但不限于:
Enzymes
酶
Monoclonal antibodies
单克隆抗体
Antibody-drug conjugates
抗体药物偶联物
Fusion proteins (e.g., antibody Fc region-containing fusion proteins)
融合蛋白(如含抗体 Fc 区的融合蛋白)
Growth factors
生长因子
Cytokines (e.g., interleukins, interferons, tumor necrosis factors)
细胞因子(如白细胞介素、干扰素、肿瘤坏死因子)
Botulinum toxins
肉毒毒素
Insulin and insulin analogues
胰岛素及其类似物
Synthetically derived proteins
合成衍生蛋白质
This compliance program applies to the manufacture of APIs intended to be sterile only up to the point immediately before the API is rendered sterile. However, neither this compliance program nor ICH Q7 provide guidance on the sterilization and aseptic processing for sterile APIs. Investigators should use compliance program 7356.002A-Sterile Drug Process Inspections and the guidance for industry on aseptic processing, Sterile Drug Products Produced by Aseptic Processing-Current Good Manufacturing Practice (September 2004), when inspecting the sterile processing of APIs that are purported to be sterile (including for compounding sterile preparations).
本程序适用于拟无菌 API 的生产,但仅覆盖至 API 灭菌前的环节。本程序及 ICH Q7 均未提供无菌 API的灭菌及无菌工艺指南。检查声称无菌的 API 的无菌工艺(包括无菌配制制剂)时,检查人员应遵循合规程序 7356.002A《无菌药品生产过程检查》及《无菌工艺生产的无菌药品 - 当前良好生产规范》(2004 年 9月)。
Bulk finished products are manufactured similarly to APIs, but they do not undergo further processing or compounding after their synthesis, fermentation, or extraction and are instead repackaged into market containers. Bulk finished products are subject to the requirements of parts 210 and 211. The synthesis and fermentation processes that result in such APIs are covered by this program rather than the program for dosage forms (i.e., compliance program 7356.002-Drug Manufacturing Inspections).
散装成品的生产方式与 API 类似,但其合成、发酵或提取后不再经进一步加工或配制,仅重新包装至市售容器。散装成品需遵守 21 CFR 第 210 和 211 部分的要求,其合成和发酵过程由本程序覆盖,而非剂型相关程序(即合规程序 7356.002《药品生产检查》)。
PART II – IMPLEMENTATION
第二部分-实施
1. Objective
1目标
The primary objective of this compliance program is to provide comprehensive CGMP inspectional coverage of API manufacturing establishments. This is done through system-based inspections that represent all profile classes (i.e., types of API manufacturing processes) and determine whether a manufacturer is operating in a state of control. An API manufacturer is operating in a state of control when it employs conditions and practices that ensure compliance with section 501(a)(2)(B) of the FD&C Act. A firm that is in a state of control produces APIs that have an adequate level of assurance of quality, identity, and purity.
本程序的主要目标是全面覆盖 API 生产机构的 CGMP 检查,通过基于系统的检查涵盖所有工艺类别(即API 生产工艺类型),并判定制造商是否处于受控状态。当 API 制造商的条件和实践符合《FD&C 法案》第 501 (a)(2)(B) 条时,即处于受控状态,其所生产的 API 具有充分的质量、标识和纯度保证。
A firm is not in a sufficient state of control if any system is significantly noncompliant with CGMP requirements such that the quality, identity, and purity of the API cannot be adequately ensured. Documented CGMP deficiencies provide the evidence for concluding that a system is not operating in a state of control. See Part V - Regulatory/Administrative Strategy, for a discussion of compliance actions based on inspection findings that demonstrate that a system or multiple systems are not in a state of control.
若任何系统严重违反 CGMP 要求,导致无法充分保证 API 的质量、标识和纯度,则企业未处于充分受控状态。有记录的 CGMP 缺陷是判定系统失控的依据。基于检查发现的单系统或多系统失控情况所采取的合规措施,详见第五部分《监管 / 行政策略》。
Profile classes generalize inspectional coverage from a small number of specific APIs to all APIs in that class. This compliance program uses a systems-based approach to further generalize inspectional coverage from a small number of profile classes to an overall evaluation of the firm. This allows preapproval inspections to focus on the specific issues related to a given drug application and improves the assessment process by providing timely and efficient support for drug application decisions.
工艺类别将检查覆盖范围从少量特定 API 扩展至该类别下所有 API。本程序采用基于系统的方法,进一步将覆盖范围从少量工艺类别扩展至企业整体评估,使批准前检查可聚焦于特定药品申请的相关问题,并为申请决策提供及时高效的支持。
Investigators should use this compliance program’s system definitions and organization when inspecting API manufacturers and reporting the results. Focusing on systems, rather than just profile classes, increases the efficiency of inspections, because the systems are oftenapplicable to multiple profile classes. An inspection under this program is profileable and will result in a determination of acceptability or nonacceptability for all API profile classes specified in this compliance program. Inspection coverage should represent all of the API profile classes that are manufactured by the firm.
检查人员检查 API 制造商及报告结果时,应采用本程序的系统定义和架构。聚焦系统而非仅关注工艺类别可提高检查效率,因系统通常适用于多个工艺类别。本程序下的检查可形成概况结论,对所有指定的 API 工艺类别做出可接受或不可接受的判定,且覆盖范围应代表企业生产的所有 API 工艺类别。
The other objectives of this compliance program include:
本程序的其他目标包括:
Determining whether inspected establishments are operating in compliance with applicable CGMP requirements to aid in FDA’s enforcement of the FD&C Act.
判定被检查机构是否遵守适用的 CGMP 要求,以支持 FDA 执行《FD&C 法案》。
Initiating appropriate action against manufacturers that are found to be out of compliance.
对不合规制造商采取适当措施。
Obtaining information that may affect other drug manufacturing or compounding operations(e.g., sterilization, drug product manufacturing, drug product compounding).
获取可能影响其他药品生产或配制操作(如灭菌、成品药生产、药品配制)的信息。
Providing guidance to manufacturers during inspections to improve compliance with CGMPrequirements, as applicable.
检查中为制造商提供指导,以提高其 CGMP 合规性(如适用)。
2. Program Management Instructions
程序管理说明
CDER uses a risk-based site selection model to identify API firms for OII’s routine surveillance inspections. CDER and OII maintain drug profiles per Chapter 5 of the Investigations Operations Manual (IOM).
CDER 采用基于风险的场地选择模型,为 OII 的常规监督检查确定 API 企业。CDER 和 OII 根据《调查操作手册》(IOM)第 5 章维护药品概况。
Unless specifically directed by CDER, OII is responsible for determining the depth of inspectional coverage for each API firm using this compliance program’s instructions. CGMP inspectional coverage under this program will be sufficient to assess the state of compliance for each firm.
除非 CDER 另有明确指示,OII 负责根据本程序要求确定各 API 企业的检查深度。本程序下的 CGMP 检查覆盖范围应足以评估各企业的合规状态。
Inspections of API manufacturers should be conducted by experienced investigators with sufficient education and training related to the type of API production process or processes conducted by the API manufacturer (e.g., fermentation, chemical synthesis). Chemists and microbiologists should be considered for inclusion on API inspection teams, as appropriate, particularly for evaluating laboratory operations (e.g., analytical methods evaluation, analytical data, laboratory procedures, instrumentation) and assessing analytical methods that are used to establish impurity profiles, fermentation manufacturing processes, and complex multistep processes for chemical synthesis.
API 制造商的检查应由经验丰富的检查人员执行,其需接受过与 API 生产工艺类型(如发酵、化学合成)相关的充分教育和培训。应酌情纳入化学家及微生物学家组成检查团队,尤其在评估实验室操作(如分析方法评价、分析数据、实验室程序、仪器)及用于建立杂质概况、发酵工艺和复杂多步化学合成的分析方法时。
Investigators conducting API inspections must understand the basic differences between theprocesses used to produce APIs and the processes used to produce finished dosage forms.APIs are usually produced by chemical synthesis or by cell culture and extraction. Thus, API production typically involves significant changes to the starting materials or intermediates by various chemical, physical, and biological processing steps. Generally, the ultimate objective in API production is to achieve a pure compound of certain identity. In contrast,the ultimate objective of finished dosage form manufacturing is generally to achieve the uniform distribution of an API across dosing units to deliver a precise amount of API.
执行 API 检查的检查人员必须理解 API 与成品剂型生产工艺的基本差异。API 通常通过化学合成或细胞培养及提取生产,其过程涉及通过化学、物理和生物步骤对起始物料或中间体进行显著改造,最终目标是获得特定标识的纯化合物。而成品剂型生产的最终目标通常是实现 API 在剂量单位中的均匀分布,以递送精确剂量。
There are two basic types of CGMP inspections: surveillance and for-cause. Surveillance inspections are conducted on a routine basis to satisfy FDA’s responsibilities to inspect drug manufacturing facilities. For-cause inspections are conducted in response to violative surveillance inspections and when a need arises to inspect a facility in response to specific events or information.
CGMP 检查主要分为两类:监督检查和针对性检查。监督检查为常规检查,以履行 FDA 对药品生产设施的检查职责;针对性检查针对违规的监督检查结果,或在需响应特定事件或信息时开展。
For-cause inspections include: (1) follow-up CGMP compliance inspections to verify corrective actions after a regulatory action has been taken; and (2) CGMP inspections in response to specific events or information (e.g., field alert reports, biological product defect reports, industry complaints, recalls, other indicators of defective products) that bring the compliance or quality of a manufacturing practice, facility, process, or API into question.
针对性检查包括:(1)监管措施后的后续 CGMP 合规检查,以验证纠正措施;(2)响应特定事件或信息(如现场警报报告、生物制品缺陷报告、行业投诉、召回、其他产品缺陷迹象)的 CGMP 检查,此类事件或信息使生产实践、设施、工艺或 API 的合规性或质量受到质疑。
Follow-up CGMP compliance inspections provide focused coverage, including the areas of concern, the proposed corrective action plan for affected operations, any implemented corrective actions, and/or the deficiencies noted on Form FDA 483–Inspectional Observations for a previous inspection. System coverage can be added on a case-by-case basis. Follow-up CGMP compliance inspections to a warning letter or other significant regulatory actions are also considered for-cause inspections and, as a result, the related for-cause assignmentscan request either full systems coverage or individual system coverage. In addition, coverage can be added on a case-by-case basis, at OII’s discretion, before or during the inspection.
后续 CGMP 合规检查聚焦于关注领域、受影响操作的拟议纠正行动计划、已实施的纠正措施及 / 或上一次检查中 FDA 483 表《检查观察结果》所列缺陷,可酌情增加系统覆盖。针对警告信或其他重大监管措施的后续检查亦属针对性检查,相关任务可要求全面系统覆盖或单个系统覆盖,OII 可在检查前或检查中酌情增加覆盖范围。
Other for-cause inspections (e.g., inspections due to industry complaints or other indicators of defective APIs) may be initiated, but these inspections can be expanded to include CGMP coverage for the purpose of updating the firm’s overall compliance status.
其他针对性检查(如因行业投诉或 API 缺陷迹象开展的检查)可扩展至 CGMP 覆盖范围,以更新企业整体合规状态。
This is the general scheme of systems for inspecting API manufacturers:
以下是 API 制造商检查的系统总体框架:
1.Quality System ensures overall compliance with CGMP requirements and internal procedures and specifications. A robust quality system relies on documentation and strong senior management oversight of CGMP operations and quality-related matters, supports and facilitates the activities conducted under all of the six systems, monitors its effectiveness, and ensures a commitment to an established quality policy.
质量系统:确保全面遵守 CGMP 要求及内部程序和规格。健全的质量系统依赖于 CGMP 操作及质量相关事项的文件记录和强有力的高级管理层监督,支持并促进其他六个系统的活动,监控其有效性,并确保对既定质量方针的承诺。
2.Facilities and Equipment System includes activities which provide an appropriate physical environment and equipment used in the production of APIs.
设施与设备系统:包括提供适宜的物理环境及 API 生产所用设备的相关活动。
3. Materials System includes measures and activities to control starting materials, intermediates, and containers.It includes validation of computerized and inventory control processes,storage, and distribution controls.
物料系统:包括控制起始物料、中间体和容器的措施及活动,涵盖计算机化和库存控制系统、储存及分销控制的验证。
4.Production System includes measures and activities to control the manufacture of APIs, including in-process sampling, testing, and process validation.
生产系统:包括控制 API 生产的措施及活动,含过程中采样、测试和工艺验证。
5.Packaging and Labeling System includes measures and activities that control the packaging and labeling of intermediates and APIs.包装与贴标签系统:包括控制中间体和 API 包装及贴标签的措施及活动。
6.Laboratory Control System includes measures and activities related to laboratory procedures, testing, analytical methods development, analytical methods validation or verification, and the stability program.
实验室控制系统:包括与实验室程序、测试、分析方法开发、分析方法验证或确认及稳定性方案相关措施及活动。
Inspectional Section III.1.B has detailed inspection coverage guidance for these systems.
第三部分第 1.B 节提供这些系统的详细检查覆盖指南。
An inspection under this program is defined as audit coverage of two or more systems, including mandatory coverage of the quality system. Inspecting at least two systems (i.e., the quality system and one other system), or more systems if deemed necessary by OII, will provide the basis for an overall inspection classification decision.
本程序下的检查定义为对两个或多个系统的审计覆盖,包括对质量系统的强制性覆盖。检查至少两个系统(即质量系统及另一个系统),或 OII 认为必要时检查更多系统,将作为整体检查分类决策的依据。
Coverage of a system should be sufficiently detailed and specific examples should be selected. Sufficient coverage ensures that the system inspection outcome reflects the system’s state of control for every profile class. If a particular representative system is adequate, it should be adequate for all drug profile classes manufactured by the firm. In some circumstances, it may not be possible to generalize certain deficiencies in a system to all API profile classes. If so, the unaffected profile classes may be considered acceptable if they are otherwise acceptable.
对一个系统的覆盖应足够详细,并选择具体示例。充分覆盖可确保系统检查结果反映每个工艺类别的系统受控状态。若某个代表性系统是充分的,则其应适用于企业生产的所有药品工艺类别。在某些情况下,可能无法将系统中的特定缺陷推广至所有 API 工艺类别,此时若未受影响的工艺类别在其他方面符合要求,则可视为可接受。
If a selected API has a unique processing or control function that is part of a system that was not chosen for coverage, the unique function can be covered for that API. However, the system for the unique function does not need to be given full coverage. For example, if an API chosen for coverage uses only high purity water in its manufacture, the water purification system can be inspected without giving full inspection coverage to the materials system. Selecting unique functions within a system will be at the discretion of the investigator.
若所选 API 具有属于未被选择覆盖的系统的独特加工或控制功能,可针对该 API 覆盖此独特功能,但无需全面覆盖该功能所属的系统。例如,若所选 API 生产仅使用高纯水,可检查水纯化系统,而无需全面覆盖物料系统。检查人员可自行决定是否选择系统内的独特功能。
Complete inspection of one system may require follow up of certain aspects of another system to fully document the findings. However, this coverage does not constitute nor require complete coverage of the other system.
完整检查一个系统可能需要跟进另一个系统的某些方面以充分记录发现,但此类覆盖不构成也不要求对另一个系统进行完整覆盖。
Inspections should cover any APIs referenced in the assignment and, as appropriate, any other representative APIs based on their level of risk. For foreign API firms, investigators should cover only APIs that are marketed or intended to be marketed in the United States.
检查应覆盖任务中提及的所有 API,并酌情覆盖基于风险水平的其他代表性 API。对于外国 API 企业,检查人员仅需覆盖在美上市或拟在美上市的 API。
Investigators should select APIs so that the coverage represents the establishment’s overall ability to manufacture in compliance with CGMP requirements. API selection should also be based on the level of risk, including selection of APIs that are:
检查人员选择的 API 应能体现机构遵守 CGMP 要求的整体生产能力,且选择应基于风险水平,包括以下API:
Used in approved drug products
用于已批准药品的 API
Therapeutically significant
具有治疗重要性的 API
Difficult to manufacture
难以生产的 API
Intended for use in parenteral or modified-release products or in combination products
拟用于注射剂、调释制剂或组合产品的 API
Documented as having past compliance problems
有记录显示存在合规问题的 API
However, this does not prevent investigators from selecting less therapeutically significant APIs to evaluate specific APIs (or profile classes) that were not previously given in-depthcoverage at the facility. Inspection coverage depth and intensity can be reduced for these APIs unless deficiencies are identified.
但这并不妨碍检查人员选择治疗重要性较低的 API,以评估设施中先前未被深入覆盖的特定 API(或工艺类别)。除非发现缺陷,否则这些 API 的检查深度和强度可降低。
When a system is inspected, the inspection of that system generally applies to all API products that use the system. Because API manufacturers are often referenced in multiple drug applications, each inspection should cover an adequate number and type of APIs to cover the selected systems. For example, if an inspection covers the production system for a site making one API by fermentation and another by synthesis, the inspection should include both types of processing in the physical inspection and the records that are sampled during the audit. This strategy, together with the classification of all applicable profile classes after the inspection, will maximize the use of FDA resources and avoid repeated visits to the same manufacturing site to cover different API profile classes.
检查一个系统时,该系统的检查结果通常适用于所有使用该系统的 API 产品。由于 API 制造商常被多个药品申请引用,每次检查应覆盖足够数量和类型的 API 以覆盖所选系统。例如,若检查覆盖某场地通过发酵生产一种 API 和通过合成生产另一种 API 的生产系统,则实地检查和审计抽样记录应包含这两种工艺类型。该策略结合检查后对所有适用工艺类别的分类,可最大限度利用 FDA 资源,避免为覆盖不同 API 工艺类别而多次访问同一生产场地。
Profile class codes or APIs selected for coverage should represent all of the APIs manufactured at the firm. Profile class codes may also be grouped by similarity, such that coverage of one profile class is sufficient to demonstrate the CGMP conditions for another profile class. For example, inspecting a profile class code of CSS could provide surrogate coverage of CSN. Similarly, inspecting a profile class code of CBI could provide surrogate coverage of other profile classes, such as CFN, CFS, and perhaps CEX.
所选工艺类别代码或 API 应代表企业生产的所有 API。工艺类别代码可按相似性分组,因此对一个工艺类别的覆盖足以证明另一个工艺类别的 CGMP 状况。例如,检查 CSS 工艺类别代码可替代覆盖 CSN;同样,检查 CBI 工艺类别代码可替代覆盖 CFN、CFS 或许还有 CEX 等其他工艺类别。
The inspection findings will be used to update all applicable profile classes. Normally, an inspection under this system approach will result in all applicable profile classes being updated. For more information, see Exhibit 5-14 Profiling a Firm’s CGMP/QS Compliance Status in the IOM.
检查结果将用于更新所有适用的工艺类别。通常,基于此系统方法的检查将更新所有适用的工艺类别。更多信息参见《调查操作手册》中的附件 5-14《企业 CGMP/QS 合规状态概况》。
PART III – INSPECTIONAL
第三部分-检查
1. Operations
操作
Investigators conducting API inspections should understand the general inspection strategy in this compliance program. API firms vary greatly in size, diversity of operations, and quality assurance systems, so investigators should carefully plan their inspection strategy at each firm. See Part III.1.C for the procedures for preparing an inspection strategy.
进行 API 检查的检查人员应理解本合规程序中的总体检查策略。API 企业在规模、运营多样性和质量保证体系方面差异很大,因此检查人员应仔细规划在每个企业的检查策略。制定检查策略的程序详见第三部分第 1.C节。
Investigators should also review the firm’s rationale for the point at which API production begins, as described in ICH Q7 and the ICH guidance for industry Q11 Development and Manufacture of Drug Substances (November 2012). This point may vary based on the type of process used for the API (e.g., synthesis, fermentation, extraction, purification).
检查人员还应审核企业关于 API 生产起始点的理由,如 ICH Q7 及 ICH 行业指南 Q11《活性药物成分的开发和生产》(2012 年 11 月)所述。该起始点可能因 API 所用工艺类型(如合成、发酵、提取、纯化)而异。
Surveillance inspections have two inspection options: a full inspection and an abbreviated inspection. For-cause inspections can provide focused coverage, or they can be expanded toabbreviated or full inspections on a case-by-case basis, at OII’s discretion.
监督检查有两种选择:全面检查和简化检查。针对性检查可提供聚焦覆盖,或 OII 可酌情将其扩展为简化检查或全面检查。
(1) Full Inspection Option
全面检查选项
The full inspection option is a CGMP inspection that provides a broad and in-depth evaluation of the establishment’s conformance with CGMP requirements. A full inspection maychange to an abbreviated inspection with concurrence from OII.
全面检查是对机构遵守 CGMP 要求情况进行广泛而深入评估的 CGMP 检查。经 OII 同意,全面检查可改为简化检查。
During the course of a full inspection, coverage in other systems may be needed to verify quality system activities. The full inspection option should include an inspection of at least four systems, one of which must be the quality system.
全面检查过程中,可能需要覆盖其他系统以验证质量系统活动。全面检查应包括至少四个系统的检查,其中一个必须是质量系统。
A full inspection is appropriate for the following cases:
全面检查适用于以下情况:
For an initial inspection of a newly registered establishment. Inspection coverage should include all the systems that are appropriate for the operations.
对新注册机构的首次检查。检查覆盖范围应包括所有适合其运营的系统。
When the establishment has a history of fluctuating into and out of compliance. To determine if the establishment meets this criterion, OII should use all of the information at itsdisposal. This information can include inspection results, results of sample analyses, complaints, defects, drug quality reports, field alert reports, adverse event reports, and recalls, inaddition to any compliance actions resulting from these types of information or from past inspections.
机构有合规状态反复波动的历史。OII 应利用所有可用信息判定机构是否符合此标准,包括检查结果、样品分析结果、投诉、缺陷、药品质量报告、现场警报报告、不良事件报告、召回,以及由这些信息或过去检查导致的任何合规措施。
To evaluate whether important changes have occurred by comparing current operations against the EIR from the last full inspection. The following are typical types of changes that warrant the full inspection option:
通过将当前运营与上次全面检查的 EIR 比较,评估是否发生重大变化。以下是值得进行全面检查的典型变化:
-Changes that introduce a new potential for cross-contamination through the type of materials that use the same equipment or the type of processing.
通过使用相同设备的物料类型或工艺类型引入新的交叉污染风险的变化。
-Use of new technology requiring new expertise, significant equipment changes, or new facilities.
使用需要新专业知识、重大设备变更或新设施的新技术。
When OII management or CDER requests this option.
OII 管理层或 CDER 要求此选项时。
To follow up on a warning letter or other regulatory actions.
跟进警告信或其他监管措施时。
When, at OII’s discretion, a full inspection needs to be conducted based on CGMP findings.
OII 根据 CGMP 检查结果酌情决定需要进行全面检查时。
(2) Abbreviated Inspection Option
简化检查选项
The abbreviated inspection option is a CGMP inspection that efficiently updates the evaluation of and provides documentation for an establishment’s conformance with CGMP requirements. The abbreviated inspection option should include an inspection audit of two to three systems, one of which must be the quality system. OII’s division management should ensure that the optional systems are rotated in successive abbreviated inspections. During the course of an abbreviated inspection, verification of quality system activities may require limited coverage in other systems.
简化检查是高效更新对机构遵守 CGMP 要求情况的评估并提供相关文件的 CGMP 检查。简化检查应包括对两到三个系统的检查审计,其中一个必须是质量系统。OII 的部门管理层应确保在连续的简化检查中轮换可选系统。简化检查过程中,验证质量系统活动可能需要对其他系统进行有限覆盖。
An abbreviated inspection is appropriate when a full inspection is not warranted. This option involves inspecting the manufacturer to: (1) maintain surveillance over the establishment’s manufacturing practices and quality performance; and (2) evaluate whether the establishment is maintaining and improving the CGMP level of assurance for the quality of its APIs. Select the abbreviated inspection option (with OII concurrence) when an establishment has:
当无需全面检查时,简化检查是适当的。该选项通过检查制造商以:(1)持续监督机构的生产实践和质量绩效;(2)评估机构是否维持并提高 API 质量的 CGMP 保证水平。经 OII 同意,当机构符合以下条件时选择简化检查:
A record of sustained acceptable compliance history
有持续可接受的合规历史记录
A strong risk management program
有强有力的风险管理计划
A lack of significant marketed API quality defects.
无重大市售 API 质量缺陷
An abbreviated inspection may be changed to a full inspection at OII’s discretion.
OII 可酌情将简化检查改为全面检查。
This section provides a complete description of each system and the areas for coverage. Investigators should take the firm’s specific operating conditions, history of previous coverage, and history of CGMP compliance into consideration when selecting systems and determining the relative depth of the audit’s coverage.
本节提供每个系统的完整描述及覆盖领域。检查人员选择系统和确定审计覆盖的相对深度时,应考虑企业的具体运营条件、先前覆盖历史和 CGMP 合规历史。
The organization and personnel (including appropriate qualifications and training), employed in any given system, will be evaluated as part of that system’s operation. Production, control, or distribution records are required to maintain CGMP compliance, and the recordsselected for review should be included for inspection audit within the context of each of the systems. Inspection of contract companies should include (1) coverage within the system for which the intermediate, API, or service is contracted; and (2) evaluation of their quality system.
任何系统中的组织和人员(包括适当的资质和培训)将作为该系统运营的一部分进行评估。生产、控制或分销记录是维持 CGMP 合规性所必需的,所选审查记录应纳入每个系统的检查审计范围。对合同公司的检查应包括(1)对中间体、API 或所承包服务所属系统的覆盖;(2)对其质量系统的评估。
Each of the following system descriptions has a bulleted list of areas. The firm should have written and approved procedures and documentation for each of these areas. Whenever possible, investigators should verify (through observation) if firms are adhering to written procedures. For each system, the areas are not limited to the final API but may also include starting materials and intermediates. All areas under each system should be covered; however, the depth of coverage may vary from the planned inspection strategy depending on inspectional findings.
以下每个系统描述均包含带项目符号的领域列表。企业应为每个领域制定书面且经批准的程序和文件。检查人员应尽可能通过观察验证企业是否遵守书面程序。每个系统的领域不仅限于最终 API,还可能包括起始物料和中间体。每个系统下的所有领域都应被覆盖,但覆盖深度可能根据检查结果与计划检查策略有所不同。
(1) Quality System
质量系统
The quality system is assessed in two phases. In phase one, investigators evaluate whether the quality unit has fulfilled the responsibility to review and approve all procedures related to production, quality control, and quality assurance. Additionally, investigators will evaluate if the quality unit has ensured that the procedures and the associated record keeping systems are adequate for their intended use. In phase two, investigators assess the data and identify any quality problems. This phase may link to other major systems for inspectional coverage.
质量系统的评估分为两个阶段。第一阶段,检查人员评估质量部门是否履行了审核和批准所有与生产、质量控制和质量保证相关的程序的职责,还将评估质量部门是否确保这些程序及相关记录保存系统适合其预期用途。第二阶段,检查人员评估数据并识别任何质量问题,此阶段可能与其他主要系统的检查覆盖相关联。
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area,they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Quality oversight of contracted operations and material suppliers
对承包运营和物料供应商的质量监督
- An effective monitoring strategy has been implemented; incoming material monitoring, life cycle qualification program, quality agreements, and timely communication mechanisms are implemented.
已实施有效的监控策略;已实施来料监控、生命周期确认计划、质量协议和及时的沟通机制。
Management oversight of the development, implementation, monitoring, and continual improvement of the quality system
对质量系统的开发、实施、监控和持续改进的管理监督
-Quality risk management and knowledge management are incorporated (e.g., timely and effective communication, appropriate resource allocation, reviews of process performance and API quality).
已纳入质量风险管理和知识管理(例如,及时有效的沟通、适当的资源分配、过程性能和 API 质量审查)。
lQuality oversight of hazards (e.g., cross-contamination, adulteration, hazardous impurities such as nitrosamines and nitrosating agents)
对危害(如交叉污染、掺假、有害杂质(如亚硝胺和亚硝化剂))的质量监督
-Hazards are documented, identified, evaluated, addressed, communicated, and continually reviewed (as needed) throughout the API’s life cycle.
在 API 的整个生命周期中,危害得到记录、识别、评估、处理、沟通,并在需要时进行持续审查。
-Hazardous impurity risks are assessed, and control strategies are implemented to mitigate the risks (e.g., actions to address sources of variability, release testing, reduction or elimination of impurities, cleaning validation); control strategies are reviewed following changes and throughout the API’s life cycle.
对有害杂质风险进行了评估,并实施了控制策略以降低风险(如针对变异性来源、放行测试、减少或消除杂质、清洁验证的行动);在变更后和整个 API 生命周期中对控制策略进行审查。
Adequate staffing to ensure fulfillment of quality unit duties
足够的人员配置以确保履行质量部门职责
Periodic quality reviews as described in ICH Q7 ICH
Q7 中所述的定期质量审核
-Reviews are complete and conducted at least annually; API quality is reviewed to assess risk and determine the need for changes, such as changes in API specifications, manufacturing, or control procedures; statistical analysis is conducted to identify areas (e.g., trends, patterns, correlations,anomalies) for action and improvement.
审核完整且至少每年进行一次;对 API 质量进行审核以评估风险并确定是否需要变更(如 API 规格、生产或控制程序的变更);进行统计分析以识别需要采取行动和改进的领域(如趋势、模式、相关性、异常)。
Complaint reviews (quality and medical)
投诉审核(质量和医疗方面)
-Reviews are documented, evaluated, and investigated in a timely manner; corrective action is included when appropriate.
–审核有记录、经过评估并及时调查;适当时包括纠正措施。
Discrepancies, failures, and critical deviations related to manufacturing and testing
与生产和测试相关的差异、失败和关键偏差
-These issues are documented and investigated in a timely manner using scientific evidence to identify the root cause; including corrective actions and preventive actions, and the effectiveness of the corrective and preventative actions is evaluated; investigations are expanded to include any related APIs or materials.
这些问题有记录并及时调查,使用科学证据确定根本原因;包括纠正措施和预防措施,并评估纠正和预防措施的有效性;调查范围扩大到包括任何相关的 API 或物料。
Stability failures
稳定性失败
-Investigation is expanded where warranted; disposition is documented; stability data supports the API retest dates and storage conditions.
在必要时扩大调查范围;处置有记录;稳定性数据支持 API 的复验日期和储存条件。
Change management for the manufacturing of all APIs
所有 API 生产的变更管理
-Changes are documented (with justification), reviewed by subject matter experts, approvedbefore implementation, and evaluated for effectiveness; changes are revalidated, reverified, and requalified as needed; quality risk management is used to evaluate proposed changes for potential risks (e.g., hazardous impurities) and impact on API quality; changes are reported to FDA by the drug application or drug master file (DMF) holder, as appropriate.
–变更有记录(附有理由),由主题专家审核,在实施前获得批准,并评估其有效性;根据需要对变更进行重新验证、重新确认和重新确认;使用质量风险管理评估拟议变更的潜在风险(如有害杂质)及其对 API 质量的影响;由药品申请或药品主文件(DMF)持有人酌情向 FDA 报告变更。
Reporting of changes for approved drug application products已批准药品申请产品的变更报告
-Changes to established conditions are documented and communicated to the drug application holder, as appropriate. This enables reporting that is compliant with relevant regulationsand consistent with the product life cycle management document in the drug application or recommendations in relevant guidance.
对既定条件的变更有记录,并酌情传达给药品申请持有人。这使得报告符合相关法规,并与药品申请中的产品生命周期管理文件或相关指南中的建议一致。
Rejects
拒收
-Investigations are expanded when warranted; corrective actions and preventative actions are implemented, when appropriate.在必要时扩大调查范围;适当时实施纠正措施和预防措施。
Quality oversight system for the release or rejection of raw materials
原料放行或拒收的质量监督系统
Batches manufactured since the last inspection to evaluate any rejections or conversions (e.g., from drug to nondrug use) because of processing problems
自上次检查以来生产的批次,以评估因加工问题导致的任何拒收或转换(如从药品用途转为非药品用途)
Recalls (including any attempt to recover distributed API not meeting its specifications or purported quality)
召回(包括任何回收不符合其规格或声称质量的已分销 API 的尝试)
-The cause was determined; corrective actions were taken.
已确定原因;已采取纠正措施。
Validation
验证
-The statuses of validation and revalidation activities (e.g., computer, manufacturing process, laboratory methods) are documented (e.g., reviews and approvals of validation protocols and reports).
–验证和再验证活动(如计算机、生产过程、实验室方法)的状态有记录(如验证方案和报告的审核和批准)。
Contemporaneous and complete documentation
同期且完整的文件记录
CGMP training and qualification for employees on a continuing basis and with sufficient frequency
持续且足够频繁地对员工进行 CGMP 培训和资质认定
-Training includes coverage of quality functions, risk management, and the specific CGMP operations assigned to individual employees.
–培训包括质量职能、风险管理以及分配给每位员工的特定 CGMP 操作的内容。
Programs for the ongoing monitoring of process performance and API quality throughout the API’s life cycle
在整个 API 生命周期中对过程性能和 API 质量进行持续监控的程序
-Significant issues are escalated to senior management.
重大问题上报给高级管理层。
Reprocess and rework
返工和再加工
-Evaluation is conducted; approval is documented; impact on validation and stability is assessed.
进行评估;批准有记录;评估对验证和稳定性的影响。
Returns and salvages
退货和回收
-Assessment is conducted; investigation is expanded where warranted; disposition is completed.
进行评估;在必要时扩大调查范围;完成处置。
(2)Facilities and Equipment System
设施与设备系统
(a) Facilities
设施
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Responsible personnel’s oversight of the facility infrastructure and the suitability of manufacturing operations
负责人员对设施基础设施和生产操作适用性的监督
Change management system for implementing changes in the facility
用于实施设施变更的变更管理系统
Facility layout, material flow, and personnel flow that prevent cross-contamination, including cross-contamination from processing of nondrug materials
防止交叉污染的设施布局、物料流和人员流,包括来自非药品物料加工的交叉污染
Complete and comprehensive separation of the manufacturing operations for highly sensitizing agents (e.g., penicillin, beta-lactams, steroids, hormones, and cytotoxics)
高致敏性物质(如青霉素、β- 内酰胺类、类固醇、激素和细胞毒素)生产操作的完全和全面分离
Qualified and appropriately monitored utilities (e.g., steam, gas, compressed air, heating, ventilation, air conditioning)
经过确认且适当监控的公用设施(如蒸汽、气体、压缩空气、供暖、通风、空调)
Lighting, potable water, washing and toilet facilities, and sewage and refuse disposal
照明、饮用水、洗涤和卫生间设施以及污水和垃圾处理
Cleaning and maintenance that potentially affect API quality
可能影响 API 质量的清洁和维护
Sanitation of the facility and use of rodenticides, fungicides, insecticides, and cleaning andsanitizing agents
设施的卫生以及灭鼠剂、杀真菌剂、杀虫剂以及清洁和消毒剂的使用
Training and qualification of personnel
人员的培训和资质认定
(b) Equipment
设备
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area, they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Equipment installation
设备安装
Equipment is operational; performance is qualified, when appropriate.
设备可运行;性能已适当确认。
Adequate equipment design, size, and location
足够的设备设计、尺寸和位置
Controls to prevent contamination, including appropriate design provisions to ensure separation from pesticides, other toxic materials, or nondrug chemicals
防止污染的控制措施,包括确保与农药、其他有毒物质或非药品化学品分离的适当设计规定
Equipment surfaces that are not reactive, additive, or absorptive in a way that could alter material quality
设备表面不会以可能改变物料质量的方式发生反应、添加物质或吸收物质
Appropriate identification of equipment (e.g., reactors, storage containers) and permanently installed processing lines
设备(如反应器、储存容器)和永久安装的加工管线的适当标识
Prevention of contact between substances associated with the operation of equipment (e.g.,lubricants, heating fluids, coolants) and starting materials, intermediates, final APIs, and containers
防止与设备操作相关的物质(如润滑剂、加热流体、冷却液)与起始物料、中间体、最终 API 和容器接触
Cleaning procedures and cleaning validation and sanitization studies to verify that residues,microbial contamination, and, when appropriate, endotoxin contamination are brought belowscientifically appropriate levels
清洁程序以及清洁验证和消毒研究,以验证残留物、微生物污染以及适当时的内毒素污染降至科学上适当的水平以下
Calibrations that use standards that can be traced to certified standards (e.g., National Institute of Standards and Technology, United States Pharmacopeia (USP))
使用可追溯至经认证标准(如美国国家标准与技术研究院、美国药典(USP))的标准进行校准
Qualification, calibration, and maintenance of storage equipment (e.g., refrigerators, freezers) to ensure that materials (e.g., standards, raw materials, reagents) are stored under appropriate conditions
储存设备(如冰箱、冰柜)的确认、校准和维护,以确保物料(如标准品、原料、试剂)在适当条件下储存
Equipment (including computers) qualification, validation, calibration, maintenance, and security
设备(包括计算机)的确认、验证、校准、维护和安全
Control system for implementing changes to equipment
用于实施设备变更的控制系统
Documentation of any discrepancies (critical discrepancy investigations are covered under the quality system)
任何差异的文件记录(关键差异调查在质量系统下涵盖)
Training and qualification of personnel
人员的培训和资质认定
(3) Materials System
物料系统
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area,they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Training and qualification of personnel
人员的培训和资质认定
Identification of starting materials and containers
起始物料和容器的标识
Storage conditions
储存条件
Quarantine of all materials and APIs (including reprocessed materials) until they are testedor examined and released
所有物料和 API(包括返工物料)在测试或检查并放行前的待验
Collection of representative samples for testing or examination
收集代表性样品进行测试或检查
-Appropriate means are used; comparisons are against appropriate specifications.使用适当的方法;与适当的规格进行比较。
A system for auditing and monitoring the suppliers of critical materials (e.g., raw materials, starting materials, intermediates) and containers
对关键物料(如原料、起始物料、中间体)和容器的供应商进行审计和监控的系统
Rejected materials
拒收的物料
-Decisions to keep or reject materials that do not meet acceptance requirements (e.g., starting materials, intermediates, containers) are documented and justified; rejected materials arepromptly quarantined and disposed.
对不符合验收要求的物料(如起始物料、中间体、容器)的保留或拒收决定有记录和理由;拒收的物料及时隔离和处置。
Appropriate retesting or reexamination of starting materials, intermediates, and containers
起始物料、中间体和容器的适当重新测试或重新检查
First in, first out use of materials and containers
物料和容器的先进先出使用
Suitability of process water used to manufacture APIs, including the water system design, maintenance, validation, and operation, as appropriate
用于生产 API 的工艺用水的适用性,包括水系统的设计、维护、验证和操作(视情况而定)
Suitability of process gas used in the manufacture of APIs (e.g., gas use to sparge a reactor), including the gas system design, maintenance, validation, and operation, as appropriate
用于 API 生产的工艺气体(如用于反应器鼓泡的气体)的适用性,包括气体系统的设计、维护、验证和操作(视情况而定)
Containers and closures that are not additive, reactive, or absorptive
非添加性、非反应性和非吸收性的容器和密封件
Change management system for implementing changes in material handling operations
用于实施物料处理操作变更的变更管理系统
-Changes in the supply chain for critical materials and containers are thoroughly evaluated,approved, and documented to ensure that they are unlikely to pose an adverse risk to APIquality.
– 对关键物料和容器供应链的变更进行彻底评估、批准和记录,以确保它们不太可能对 API 质量造成不利风险。
Qualification, validation, and security of computerized or automated processes
计算机化或自动化过程的确认、验证和安全
Distribution records by batch for all materials (e.g., the finished API, intermediates), including records for exported materials
所有物料(如成品 API、中间体)的批次分销记录,包括出口物料的记录
Documentation of any discrepancies (critical discrepancy investigations are covered under the quality system)
任何差异的文件记录(关键差异调查在质量系统下涵盖)
Risk management program for starting materials, intermediates, and containers
起始物料、中间体和容器的风险管理计划
-Unacceptable hazards (e.g., impurities) are addressed; risks are assessed, as needed, throughout the API’s life cycle.
解决不可接受的危害(如杂质);在 API 的整个生命周期中根据需要评估风险。
(4) Production System
生产系统
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area,they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Training and qualification of personnel
人员的培训和资质认定
Establishment of, adherence to, and documented performance of approved manufacturing procedures
制定、遵守经批准的生产程序并记录其执行情况
Controls for critical activities and operations
对关键活动和操作的控制
Documentation and investigation of critical deviations
关键偏差的文件记录和调查
Comparison of actual yields with expected yields at designated steps
在指定步骤将实际收率与预期收率进行比较
Process validation program that ensures a state of control across the life cycle (i.e., process design, process qualification, and continued process verification stages)
确保整个生命周期(即过程设计、过程确认和持续过程验证阶段)处于受控状态的工艺验证计划
Establishment of adequate control steps to ensure that APIs are suitable and safe for theirintended use
制定充分的控制步骤,确保 API 适合并安全用于其预期用途
-For APIs intended to be used in parenteral dosage forms, pyrogenic (e.g., endotoxin) contamination can be reduced or prevented through the use of appropriate water quality, inputmaterials, and process steps.
对于拟用于注射剂型的 API,可通过使用适当的水质、输入物料和工艺步骤来减少或防止热原(如内毒素)污染。
Established time limits for completion of phases of production, when appropriate
适当时,规定生产各阶段的完成时限
Appropriate identification of major equipment used in the production of intermediates and the API
用于生产中间体和 API 的主要设备的适当标识
Justification and consistency of intermediate specifications and API specifications
中间体规格和 API 规格的合理性和一致性
Implementation and documentation of process controls, testing, and examinations (e.g., pH,temperature, purity, actual yields, clarity)
过程控制、测试和检查(如 pH 值、温度、纯度、实际收率、澄清度)的实施和文件记录
In-process sampling that is conducted using procedures designed to prevent contamination of the sampled material
按照旨在防止被采样物料污染的程序进行过程中采样
Recovery (e.g., from mother liquor or filtrates) of reactants
反应物的回收(如从母液或滤液中)
-Approved procedures and recovered materials meet specifications that are suitable for their intended use.
经批准的程序和回收的物料符合适合其预期用途的规格。
Recovery of solvents
溶剂的回收
-Recovered solvents should be used only in the same step or in an earlier step (if there is sufficient purification) of the same processes from which they were collected.
回收的溶剂仅可用于其收集来源的相同工艺的相同步骤或更早步骤(如果经过充分纯化)。
Precautions to prevent or minimize the potential for cross-contamination when APIs are micronized on multiuse equipment当 API 在多用途设备上进行微粉化时,采取预防措施防止或最大限度地减少交叉污染的可能性
Validation and security of computerized or automated processes
计算机化或自动化流程的验证和安全
Ongoing statistical evaluations (e.g., batch control data, periodic capability analysis) to identify processes that exhibit high variability and trigger needed improvements
持续的统计评估(如批次控制数据、定期能力分析),以识别表现出高变异性的过程并触发所需的改进
Change management system for production changes, including evaluation of the need for additional validation studies
生产变更的变更管理系统,包括评估是否需要额外的验证研究
Master batch production and control records that include instructions and processes of appropriate specificity that enable production operators to reproducibly execute the same manufacturing processes each time the API is produced
主批次生产和控制记录,包括具有适当特异性的说明和过程,使生产操作员能够每次生产 API 时可重复地执行相同的生产过程
Batch production and control records
批次生产和控制记录
Contemporaneous and complete documentation of batch production
批次生产的同期且完整的文件记录
Documentation of any discrepancies (critical discrepancy investigations are covered under the quality system)
任何差异的文件记录(关键差异调查在质量系统下涵盖)
Establishment of effective control strategies for manufacturing operations that may potentially pose a risk of forming hazardous impurities
为可能存在形成有害杂质风险的生产操作制定有效的控制策略
(5) Packaging and Labeling System
包装与贴标签系统
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area,they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Training and qualification of personnel
人员的培训和资质认定
Acceptance operations for packaging and labeling materials
包装和贴标签物料的验收操作
Establishment of, adherence to, and documented performance of approved packaging and labeling procedures
制定、遵守经批准的包装和贴标签程序并记录其执行情况
Change management system for implementing changes in packaging and labeling operations
用于实施包装和贴标签操作变更的变更管理系统
Adequate storage for labels and labeling, both approved and returned after issued
已批准和发放后退回的标签和贴标签的充分储存
Control of labels with similar sizes, shapes, and colors that are used for different APIs
用于不同 API 的具有相似尺寸、形状和颜色的标签的控制
Adequate packaging records that include specimens of all labels used充分的包装记录,包括所用所有标签的样本
Control of issuance of labeling, examination of issued labels, and reconciliation of used labels标签发放的控制、所发放标签的检查以及所用标签的核对
Examination of the labeled finished APIs
对贴标签的成品API 的检查
Adequate inspection (i.e., proofing) of incoming labeling
对收到的贴标签的充分检查(即校对)
Use of lot numbers and destruction of excess labeling bearing lot or control numbers
批号的使用以及销毁带有批号或控制号的多余标签
Adequate separation and controls when more than one batch is labeled at a time
当同时对多个批次进行贴标签时的充分分离和控制
Adequate expiration or retest dates on the label
标签上充分的有效期或复验日期
Validation of packaging and labeling operations including validation and security of computerized processes
包装和贴标签操作的验证,包括计算机化过程的验证和安全
Documentation of any discrepancies (critical discrepancy investigations are covered under the quality system)
任何差异的文件记录(关键差异调查在质量系统下涵盖)
Repackaged APIs and intermediates
重新包装的 API 和中间体
-The name of and information about the original API or intermediate manufacturer, repacker, and relabeler are provided.提供原始 API 或中间体制造商、重新包装商和重新贴标签商的名称和信息。
(6) Laboratory Control System
实验室控制系统
Evaluate each of the areas listed below. If there are additional considerations for the area,they are listed in sub-bullets.
评估以下每个领域。若该领域有其他考虑因素,将在子项目符号中列出。
Training and qualification of personnel
人员的培训和资质认定
Adequate staffing for laboratory operations
实验室操作的充分人员配置
Adequate equipment and facility for the intended use
适合预期用途的充分设备和设施
Calibration and maintenance programs for analytical instruments and equipment
分析仪器和设备的校准和维护计划
Validation and security of computerized or automated processes
计算机化或自动化流程的验证和安全
Source and purity of reference standards
参考标准品的来源和纯度
Assays and tests are used to establish equivalency to current official reference standards, as appropriate.测定和测试用于确定与当前官方参考标准品的等效性(视情况而定)。
System suitability tests for chromatographic systems
色谱系统的系统适用性测试
Specifications, standards, and representative sampling plans
规格、标准和代表性采样计划
Validation or verification of analytical methods, including suitability of microbiological test methods
分析方法的验证或确认,包括微生物测试方法的适用性
Adequate test methods for establishing complete impurity profiles for each API productionprocess
用于为每个 API 生产过程建立完整杂质概况的充分测试方法
Note that impurity profiles are often process-related.
注意杂质概况通常与过程相关。
Reassessment of impurity profiles after changes that could affect the impurity profile (e.g.,new sources of raw materials or reagents)
在可能影响杂质概况的变更后(如原料或试剂的新来源)重新评估杂质概况
Change management strategy for hazardous impurities if any hazardous impurities have been identified: (1) in any starting material, intermediate, container, or the API; or (2) as a degradant during the API’s life cycle
如果在任何起始物料、中间体、容器或 API 中已识别出任何有害杂质,或在 API 的生命周期中作为降解产物识别出任何有害杂质,则针对有害杂质的变更管理策略
Change management system for implementing changes in laboratory operations
用于实施实验室操作变更的变更管理系统
Required testing of the correct samples using the approved or filed methods or equivalent methods
使用批准或备案的方法或等效方法对正确的样品进行所需的测试
Documentation of any discrepancies (critical discrepancy investigations are covered under the quality system)
任何差异的文件记录(关键差异调查在质量系统下涵盖)
Complete analytical records from all tests and summaries of results
所有测试的完整分析记录和结果摘要
Contemporaneous and complete laboratory records
同期且完整的实验室记录
Quality and retention of raw data (e.g., chromatograms, spectra)
原始数据(如色谱图、光谱)的质量和保留
Correlation of result summaries to raw data; presence and disposition of unused data
结果摘要与原始数据的相关性;未使用数据的存在和处置
Adherence to an adequate out of specification procedure that includes timely completion ofinvestigations遵守充分的超出规格程序,包括及时完成调查
Adequate reserve samples and documented examination of reserve samples
充分的留样和留样的有记录检查
Stability testing program, including demonstration that the analytical methods are stability-indicating
稳定性测试计划,包括证明分析方法具有稳定性能力
These procedures are in addition to those in the IOM.
这些程序是对《调查操作手册》中程序的补充。
1.Select two or more systems for inspection coverage, as appropriate (see Part III.1.A).
酌情选择两个或多个系统进行检查覆盖(见第三部分第 1.A 节)。
2.If APIs are not specified in the assignment, select significant APIs for inspection coverage. APIs are considered significant based on risk. Significant APIs include: (1) APIs that broadly use all of the systems in the firm or use special manufacturing features (e.g., complex chemical synthesis); and (2) APIs that are highly sensitizing materials, infectious materials, or new chemical entities made under approved drug applications. Review the firm’s inspection history, compliance history, DMF, or drug application files.
如果任务中未指定 API,则选择重要的 API 进行检查覆盖。API 的重要性基于风险确定。重要 API 包括:(1)广泛使用企业所有系统或具有特殊生产特征(如复杂化学合成)的 API;(2)高致敏性材料、传染性材料或根据已批准药品申请生产的新化学实体。审查企业的检查历史、合规历史、DMF 或药品申请文件。
3.If CDER or OII request a CDER staff member to be a member of the inspection team,the lead investigator should brief them on the intended inspection strategy and explain their supporting role and responsibilities for the inspection. The lead investigator should consult with OPQ assessors on any specific drug application chemistry, manufacturing, or control issues (whether premarket or postmarket) that will be covered during the inspection.
如果 CDER 或 OII 要求 CDER 工作人员加入检查团队,首席检查人员应向他们简要介绍预期的检查策略,并说明他们在检查中的支持角色和职责。首席检查人员应就检查期间将涵盖的任何特定药品申请的化学、生产和控制问题(无论是上市前还是上市后)咨询 OPQ 评估员。
4.Review the impurity profile for each API production process that will be covered during the inspection. If an application or DMF was submitted, compare the firm’s impurity profiles to the impurity profiles submitted.
审查将在检查期间涵盖的每个 API 生产过程的杂质概况。如果已提交申请或 DMF,将企业的杂质概况与所提交的杂质概况进行比较。
5.For the APIs that will be inspected, verify conformity to any compendial monographs, as appropriate.
对于将接受检查的 API,酌情验证其是否符合任何药典专著。
6.Before or during the inspection, determine if the firm has made process changes by comparing current operations against the EIR for the previous inspection. Also compare the current operations with those described in the DMF or the drug application to determine whether the firm is complying with the postapproval chemistry, manufacturing, and controls commitments that they made to FDA. The following are examples of changes that would warrant extensive coverage during the inspection:
在检查前或检查期间,通过将当前运营与上一次检查的 EIR 进行比较,确定企业是否进行了工艺变更。还将当前运营与 DMF 或药品申请中描述的运营进行比较,以确定企业是否遵守其向 FDA 做出的上市后化学、生产和控制承诺。以下是在检查期间值得广泛覆盖的变更示例:
a.API production process changes or product-type line changes that include processing of several APIs of varying toxicity in common equipment and/or facilities. These changes could introduce new potential cross-contamination.
API 生产工艺变更或产品线变更,包括在共同设备和 / 或设施中加工多种不同毒性的 API。这些变更可能引入新的潜在交叉污染。
b.New technology that requires new expertise, significantly new equipment, or new facilities.
需要新专业知识、显著新设备或新设施的新技术。
c.Changes (particularly those that are not referenced in the DMF or drug application) in starting materials, intermediates, equipment, facilities, support systems, processing steps, packaging materials, or computer software.
起始物料、中间体、设备、设施、支持系统、加工步骤、包装材料或计算机软件的变更(特别是那些未在 DMF 或药品申请中提及的变更)。
7.For foreign firms, obtain file information from the appropriate CDER assessment division or compliance unit.Investigators may also request background information about the site directly from the U.S. Agent before the inspection.
对于外国企业,从适当的 CDER 评估部门或合规单位获取文件信息。检查人员还可在检查前直接向美国代理请求该场地的背景信息。
2. Reporting
报告
Investigators should describe their inspection coverage and findings in the EIR. Investigators should include a sufficient level of detail for further FDA evaluation of the firm’s state of control and conformance to CGMP requirements. ICH Q7 may be used as a guideline to describe coverage, findings, and deficiencies. However, investigators should not reference specific sections of ICH Q7 in the Form FDA 483 observations or in the EIR. If an investigator believes that a particular practice consistent with ICH Q7 is deficient, the investigator or division should consult with CDER’s Office of Manufacturing Quality (OMQ) before making an observation that conflicts with ICH Q7.
检查人员应在 EIR 中描述其检查覆盖范围和发现。检查人员应提供足够详细的信息,供 FDA 进一步评估企业的受控状态和对 CGMP 要求的符合性。ICH Q7 可用作描述覆盖范围、发现和缺陷的指南。然而,检查人员不应在 FDA 483 表观察结果或 EIR 中引用 ICH Q7 的具体章节。如果检查人员认为符合 ICH Q7 的特定做法存在缺陷,检查人员或部门应在做出与 ICH Q7 冲突的观察结果之前咨询 CDER 的生产质量办公室(OMQ)。
The Form FDA 483, if issued, should include sections for each of the covered systems. In addition to the IOM format and information reporting requirements, all EIRs for API manufacturers must include:
如发布 FDA 483 表,应包含每个被覆盖系统的部分。除《调查操作手册》的格式和信息报告要求外,所有API 制造商的 EIR 必须包括:
1.A list of APIs manufactured (or categories of APIs if there are several APIs) along with the general manufacturing process for each API (e.g., chemical synthesis, fermentation, extraction of botanical material).
所生产 API 的列表(或 API 类别,如果有多个 API)以及每种 API 的一般生产过程(如化学合成、发酵、植物材料提取)。
2.An explanation for the APIs selected for coverage.
对所选 API 进行覆盖的解释
3.For foreign API manufacturers, the U.S. Agent’s name, title, complete mailing address, telephone number, and fax number or email address.
对于外国 API 制造商,美国代理的姓名、头衔、完整邮寄地址、电话号码以及传真号码或电子邮件地址。
4.For foreign API manufacturers, a report of all APIs imported into the United States in the last two years, their consignees (including in-country intermediary repackers, relabelers, wholesalers, distributors, and shippers that import directly in the U.S.), and an estimate of the frequency and quantity of shipments to these consignees.
对于外国 API 制造商,过去两年中所有进口到美国的 API 的报告、其收货人(包括国内中间重新包装商、重新贴标签商、批发商、分销商和直接进口的托运人),以及对这些收货人的发货频率和数量的估计。
4. A description of each of the systems selected for coverage (i.e., areas, processes, and operations), what was covered, who was interviewed, and what manufacturing activities were taking place during the inspection.
对每个所选覆盖系统的描述(即领域、过程和操作)、所覆盖的内容、访谈的人员以及检查期间正在进行的生产活动。
5.Any significant changes to a firm’s packaging, labeling, product line, or processes, particularly changes that are not properly filed, submitted, or reported in a DMF or drug application (including changes to APIs intended for use in compounding).企业包装、贴标签、产品线或过程的任何重大变更,特别是那些未在 DMF 或药品申请中适当归档、提交或报告的变更(包括拟用于配制的 API 的变更)。
Investigators should instruct management to submit an electronic response to a Form FDA 483 with appropriate documentation via email to CDER-OC-OMQ-Domestic483Response@fda.hhs.gov or CDER-OC-OMQ-International483Response@fda.hhs.gov.
检查人员应指示管理层通过电子邮件向CDER-OC-OMQ-Domestic483Response@fda.hhs.gov 或CDER-OC-OMQ-International483Response@fda.hhs.gov 提交对FDA 483表的电子回复及适当文件。
For human drug inspections that include CGMP and preapproval inspectional coverage, in addition to the address above, include: CDERPAIprogram@fda.hhs.gov.
对于包括CGMP和批准前检查覆盖的人用药品检查 , 除上述地址外,还应发送至:CDERPAIprogram@fda.hhs.gov。
PART IV – ANALYTICAL
第四部分-分析
API samples that the investigator collects for quality evaluation should be submitted to theappropriate servicing laboratory. Please email the Office of the Chief Scientist (OCS)/Office of Analytical and Regulatory Laboratories (OARL) at OCOCSOARLProgramCoordinators@fda.hhs.gov to request servicing laboratories for chemical and microbiological testing. In the request, include the API description, lot numbers to be tested, analyses required, and the reason for sample collection. Servicing laboratories will be selected based on specialization, technology and testing expertise, and capacity. However, it should be noted that physical API samples are not required to support regulatory or administrative action against a violative firm or drug.
检查人员为质量评估而收集的 API 样品应提交给适当的服务实验室。请通过电子邮件向首席科学家办公室( OCS ) / 分 析 和 监 管 实 验 室 办 公 室 ( OARL ) 发 送 请 求 , 邮 箱 地 址 为 OCOCSOARLProgramCoordinators@fda.hhs.gov,请求提供用于化学和微生物测试的服务实验室。在请求中,应包括 API 描述、待测试的批号、所需的分析以及样品收集的原因。服务实验室的选择将基于专业、技术和测试专业知识以及能力。然而,应注意,支持对违规企业或药品采取监管或行政行动并不需要 API 的物理样品。
PART V–REGULATORY/ADMINISTRATIVE STRATEY
第五部分-监管 / 行政策略
If one or more systems are documented as not in a state of control, OII should endorse an OAI inspection report.
如果一个或多个系统被记录为未处于受控状态,OII 应认可 OAI 检查报告。
Normally, issuing a warning letter or taking other regulatory or administrative action should result in all profile classes being classified as unacceptable. However, if CDER does not approve a recommendation for a warning letter or other regulatory action, all profile classes should be classified as acceptable.
通常,发布警告信或采取其他监管或行政行动应导致所有工艺类别被归类为不可接受。然而,如果 CDER 不批准关于警告信或其他监管行动的建议,则所有工艺类别应被归类为可接受。
If an establishment with approved established conditions has an inspection that is classified as OAI and raises significant concerns about the quality system (particularly about the change management system), CDER offices will collaboratively evaluate the significant findings and the firm’s response. They will use this information to determine how these findings could potentially affect the approved established conditions.
如果具有已批准既定条件的机构的检查被归类为 OAI,且对质量系统(特别是变更管理系统)提出重大担忧,CDER 各办公室将合作评估重大发现和企业的回应。他们将利用这些信息确定这些发现可能如何影响已批准的既定条件。
Records, documents, and other information that are requested and reviewed during remote regulatory assessments may reveal potentially violative practices. In such cases, OMQ’s evaluation of a potential OAI recommendation will align with the procedures in this section during review of the case.
在远程监管评估期间请求和审查的记录、文件和其他信息可能揭示潜在的违规做法。在这种情况下,OMQ 对潜在 OAI 建议的评估将在审查案件期间遵循本节中的程序。
Recommendations for regulatory action for API CGMP deficiencies should cite the statute (section 501(a)(2)(B) of the FD&C Act) and not the drug product regulations in parts 210and 211. These recommendations should not cite ICH Q7; however, they can use ICH Q7as a guideline for describing the deficiencies. The regulatory action should demonstrate how the observed deficiencies could potentially impact or have already impacted the quality of the API. When evaluating whether to recommend regulatory or administrative action, consider the critical attributes of the API, the significance of its pharmacological activity, and the intended use of the drug product that will contain the API.
针对 API CGMP 缺陷的监管行动建议应引用法规(《FD&C 法案》第 501 (a)(2)(B) 条),而非第 210和211部分中的药品法规。这些建议不应引用 ICH Q7;然而,它们可以使用 ICH Q7 作为描述缺陷的指南。监管行动应证明所观察到的缺陷如何可能影响或已经影响 API 的质量。在评估是否建议采取监管或行政行动时,应考虑 API 的关键属性、其药理活性的重要性以及将包含该 API 的药品的预期用途。
Evidence that supports a significant deficiency or pattern of deficiencies within a system may indicate system failure. The failure of a system puts all of the manufacturer’s APIs at risk and should be promptly corrected. The following are examples of deficiencies that may result in an inspection that is classified as OAI:
证明系统内存在重大缺陷或缺陷模式的证据可能表明系统故障。系统故障会使制造商的所有API 面临风险,应立即纠正。以下是可能导致检查被归类为 OAI 的缺陷示例:
1.Contamination of APIs with filth, objectionable microorganisms, toxic chemicals, or significant amounts of other types of chemicals, or a reasonable potential for such contamination because of a demonstrated route of contamination (facilities and equipment system; production system).
API 受到污物、不良微生物、有毒化学品或大量其他类型化学品的污染,或由于已证明的污染途径而存在此类污染的合理可能性(设施和设备系统;生产系统)。
2.Failure to show that API batches conform to established specifications, such as specifications in drug applications, USP specifications, customer specifications, or label claims (quality system).未能证明 API 批次符合既定规格,如药品申请中的规格、USP 规格、客户规格或标签声明(质量系统)。
3.Failure to ensure the accuracy and integrity of data. Complete, consistent, and accurate data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded, original or a true copy, and accurate. Examples of data integrity concerns include failing to scientifically justify not reporting relevant data, altering of raw data, inconsistently documenting manufacturing operations, backdating test results, testing into compliance, and fabricating test results. Examples of failure to ensure the accuracy and integrity of data include systems which allow for the alteration or deletion of raw data, systems without audit trails activated, loose raw data forms without adequate issuance and reconciliation, and inadequate risk-based monitoring for data integrity concerns (all systems).
未能确保数据的准确性和完整性。完整、一致和准确的数据应可归因、清晰可读、同期记录、原始或真实副本,并且准确。数据完整性问题的示例包括未能科学证明不报告相关数据的合理性、更改原始数据、不一致地记录生产操作、追溯测试结果、测试至合格以及伪造测试结果。未能确保数据准确性和完整性的示例包括允许更改或删除原始数据的系统、未激活审计追踪的系统、没有充分发放和核对的松散原始数据表格,以及对数据完整性问题的基于风险的监控不足(所有系统)。
4.Failure to comply with commitments in drug applications or DMFs. All of the required information in these commitments should be accurate and current. This includes information about the manufacturing process, impurity profiles, and other specifications or proceduresassociated with the manufacture of the API (quality system).
未能遵守药品申请或 DMF 中的承诺。这些承诺中的所有所需信息都应准确且最新。这包括与 API 生产相关的生产过程、杂质概况以及其他规格或程序的信息(质量系统)。
5.Distribution of an API that does not conform to established specifications (quality system).
分销不符合既定规格的 API(质量系统)。
6.Deliberate blending of API batches in an attempt to: (1) dilute or hide filth or other noxious contaminants; or(2) disguise a critical quality defect and obtain a batch that meets its specifications (production system).
故意混合 API 批次,试图:(1)稀释或隐藏污物或其他有害污染物;或(2)掩盖关键质量缺陷并获得符合其规格的批次(生产系统)。
7.Failure to demonstrate that all materials (including water and any other solvents used in the final step of the API production process) are chemically and microbiologically suitable for their intended use and do not adversely affect the quality of the API (materials system).
未能证明所有物料(包括在 API 生产过程最后一步中使用的水和任何其他溶剂)在化学和微生物方面适合其预期用途,且不会对 API 质量产生不利影响(物料系统)。
8. Lack of adequate validation for critical steps in the API production process, particularly for the final separation and purification of the API or API production processes for whichthere is evidence that the process is not adequately controlled. Lack of adequate control may be indicated by repeated batch failures or wide variation in final yields compared with the process average over time (quality system; production system).
API 生产过程中关键步骤缺乏充分的验证,特别是 API 的最终分离和纯化或有证据表明过程未得到充分控制的 API 生产过程。控制不足可能表现为重复的批次失败或与过程平均值相比最终收率的广泛变化(质量系统;生产系统)。
9.Implementation of retrospective process validation for an existing API production processwhen the process has changed significantly, the firm lacks impurity profile data, or there is evidence of repeated batch failures because of process variability (quality system; production system).
当现有 API 生产过程发生重大变化、企业缺乏杂质概况数据或有证据表明由于过程变异性导致重复批次失败时,对现有 API 生产过程实施回顾性过程验证(质量系统;生产系统)。
10.Failure to establish an impurity profile for each API production process. FDA expects manufacturers to establish complete impurity profiles for each API as part of the process validation effort. This includes collecting data on: (1) actual and potential organic impurities that may arise during synthesis, purification, and storage of the API; (2) actual and potential inorganic impurities that may arise during the API production process; and (3) organic and inorganic solvents used during the manufacturing process that are known to carry over to the API. Impurity profile testing of each batch or after a specified number of batches may detect new impurities that could be from a deliberate or nondeliberate change inthe API manufacturing process (laboratory control system).
未能为每个 API 生产过程建立杂质概况。FDA 期望制造商作为过程验证工作的一部分,为每个 API建立完整的杂质概况。这包括收集以下数据:(1)在 API 合成、纯化和储存期间可能产生的实际和潜在有机杂质;(2)在 API 生产过程中可能产生的实际和潜在无机杂质;(3)在生产过程中使用的、已知会带入 API 中的有机和无机溶剂。每批或特定数量批次后的杂质概况测试可能检测到新的杂质,这些杂质可能来自 API 生产过程中的故意或非故意变更(实验室控制系统)。
11.Failure to show that a reprocessed batch complies with all of the established standards, specifications, and characteristics (quality system; laboratory control system).
未能证明返工批次符合所有既定标准、规格和特性(质量系统;实验室控制系统)。
12.Failure to test for residues of organic or inorganic solvents used during manufacturing that may carry over to the API using analytical procedures with appropriate levels of sensitivity (laboratory control system).
未能使用具有适当灵敏度水平的分析程序测试生产过程中使用的可能带入 API 中的有机或无机溶剂残留(实验室控制系统)。
13.Failure to have a formal process change control system in place to evaluate changes in starting materials, facilities, support systems, equipment, processing steps, and packaging materials that may affect the quality of APIs (all systems).
缺乏正式的过程变更控制系统来评估起始物料、设施、支持系统、设备、加工步骤和包装材料的变更可能对 API 质量产生的影响(所有系统)。
14.Failure to maintain batch and quality control records (quality system).
未能维护批次和质量控制记录(质量系统)。
15.Incomplete stability studies to establish API stability for the intended period of use, forexample, failure to conduct forced degradation studies on APIs to isolate, identify, and quantify potential degradants that may arise during storage (laboratory control system).
用于确定 API 在预期使用期限内稳定性的稳定性研究不完整,例如,未能对 API 进行强制降解研究以分离、识别和量化储存期间可能产生的潜在降解产物(实验室控制系统)。
16.Use of laboratory test methods that are inadequate or have not been validated, or the use of an inadequately qualified or untraceable reference standard (laboratory control system).
使用不充分或未经验证的实验室测试方法,或使用资质不足或不可追溯的参考标准品(实验室控制系统)。
17.Packaging and labeling in a way that introduces a significant risk of mislabeling (packaging and labeling system).
以可能导致错误贴标签的方式进行包装和贴标签(包装和贴标签系统)。