您当前的位置:检测资讯 > 科研开发
嘉峪检测网 2023-01-30 11:30
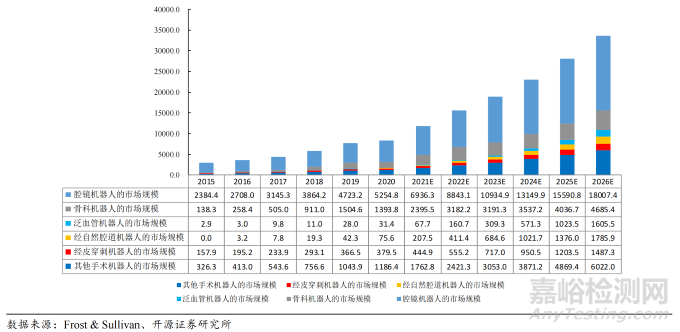
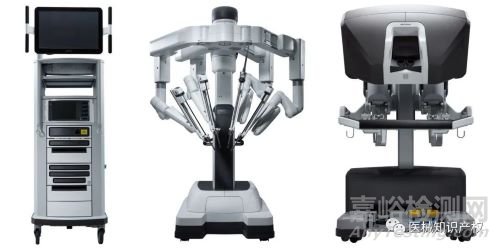
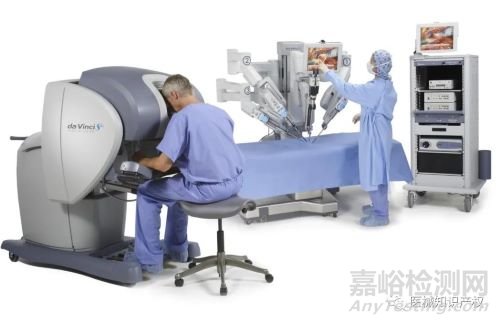
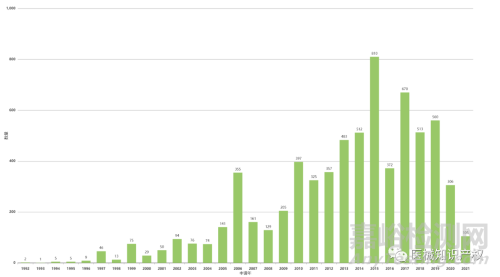
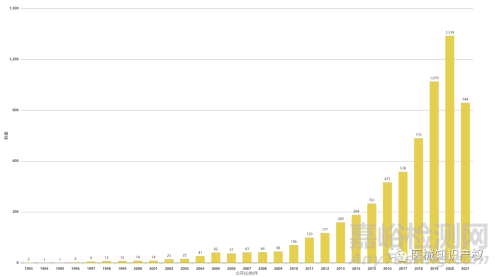
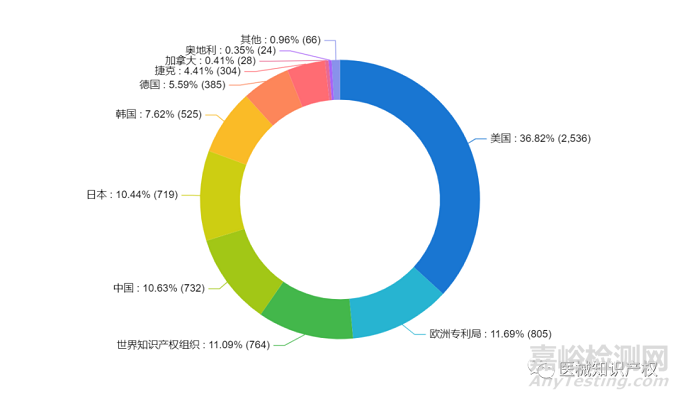
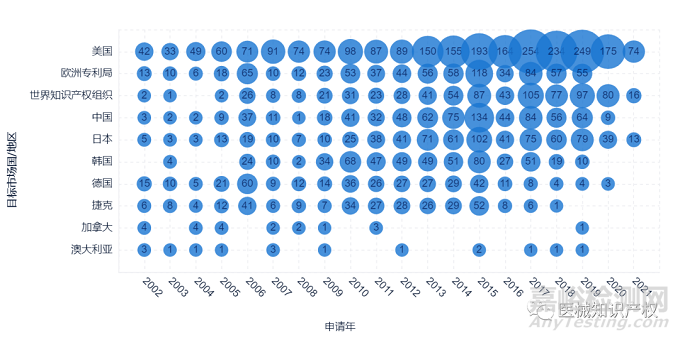
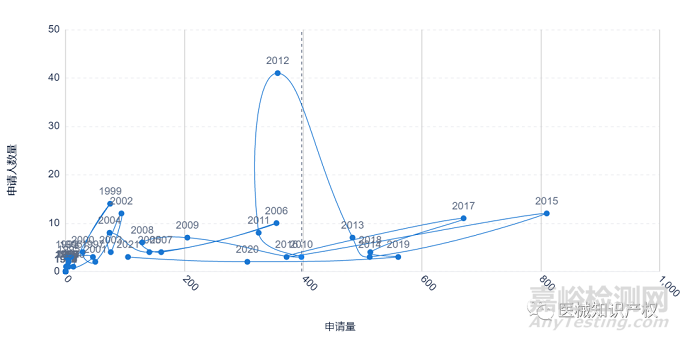
手术机器人市场概览

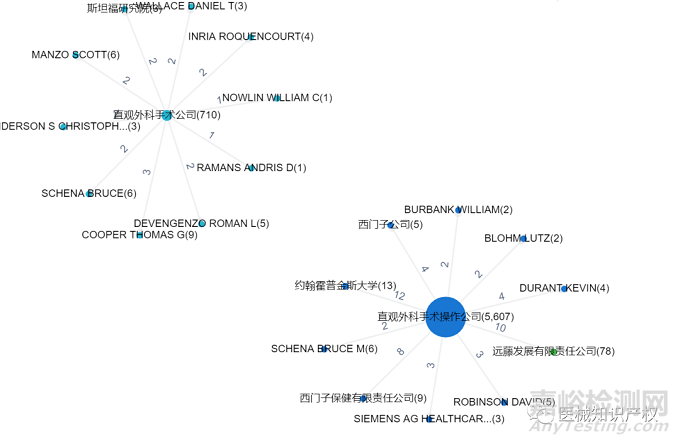
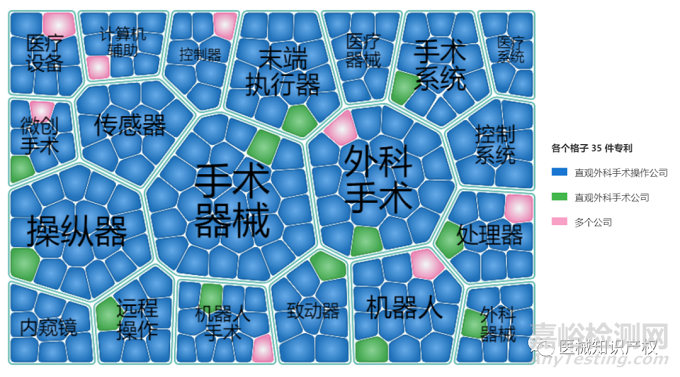
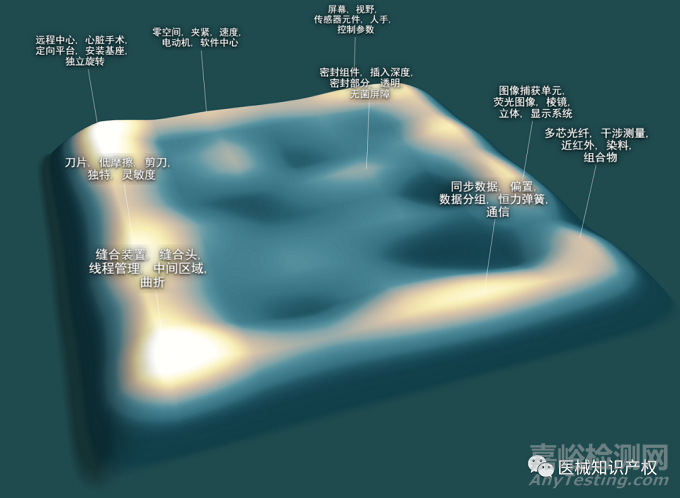

| 公开/公告号 | US5797900A | 申请日 | 1997/5/16 |
| 发明名称 | Wrist mechanism for surgical instrument for performing minimally invasive surgery with enhanced dexterity and sensitivity | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | In accordance with the above objects of the invention applicants describe a compact articulated surgical instrument suitable for endoscopic surgery. The instrument has two opposed pivoting jaws and a pivoting wrist member. The instrument is capable of providing force reflection with high'sensitivity. The instrument is adapted to be coupled via a servomechanism to a master control operated by a surgeon. | ||
| 技术方案 | An articulated surgical instrument for enhancing the performance of minimally invasive surgical procedures. The instrument has a high degree of dexterity, low friction, low inertia and good force reflection. A unique cable and pulley drive system operates to reduce friction and enhance force reflection. A unique wrist mechanism operates to enhance surgical dexterity compared to standard laparoscopic instruments. The system is optimized to reduce the number of actuators required and thus produce a fully functional articulated surgical instrument of minimum size. | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | US6905491B1 | 申请日 | 1997/5/16 | |
| 发明名称 | Apparatus for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures with a robotic arm that has a passive joint and system which can decouple the robotic arm from the input device | |||
| 解决的技术问题 | There have been attempts to perform CABG procedures without opening the chest cavity. Minimally invasive procedures are conducted by inserting surgical instruments and an endoscope through small incision in the skin of the patient. Manipulating such instruments can be awkward, particularly when suturing a graft to a artery. It has been found that a high level of dexterity is required to accurately control the instruments. Additionally, human hands typically have at least a minimal amount of tremor. The tremor further increases the difficulty of performing minimal invasive cardiac procedures. It would be desirable to provide a system for effectively performing minimally invasive coronary artery bypass graft procedures.. | |||
| 技术方案 | A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The robotic arm may contain a passive joint that provides an additional degree of freedom. Additionally, the system may include a disconnect input device that decouples the arm from an input device such as the handles. | |||
| 相关附图 |
|
|||
| 公开/公告号 | US6783524B2 | 申请日 | 2002/4/18 |
| 发明名称 | Robotic surgical tool with ultrasound cauterizing and cutting instrument | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | Surgical ultrasound instruments are generally capable of treating tissue with use of frictional heat produced by ultrasonic vibrations. For example, the heat may be use to cut and/or cauterize tissue. With many currently available instruments, tissue may first be grasped by an ultrasound surgical device and then ultrasound energy may be delivered to the tissue to cut, cauterize or the like. Ultrasound instruments provide advantages over other cutting and cauterizing systems, such as reduced collateral tissue damage, reduced risk of unwanted burns, and the like. Currently, however, ultrasound instruments for use with a robotic surgical system are not available. | ||
| 技术方案 | A surgical instrument for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes an elongate shaft with an ultrasound probe, an end effector at the distal end of the shaft, and a base at the proximal end of the shaft. The end effector includes an ultrasound probe tip and the surgical instrument is generally configured for convenient positioning of the probe tip within a surgical site by a robotic surgical system. Ultrasound energy delivered by the probe tip may be used to cut, cauterize, or achieve various other desired effects on tissue at a surgical site. In various embodiments, the end effector also includes a gripper, for gripping tissue in cooperation with the ultrasound probe tip. The base is generally configured to removably couple the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system and to transmit forces from the surgical system to the end effector, through the elongate shaft. A method for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes coupling the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system, positioning the probe tip in contact with tissue at a surgical site, and delivering ultrasound energy to the tissue. | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | US8100133B2 | 申请日 | 2006/6/28 |
| 发明名称 | Indicator for tool state and communication in multi-arm robotic telesurgery and method of use | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | While the new telesurgical systems, devices and methods have proven highly effective and advantageous, still further improvements would be desirable. In general, it would be desirable to provide improved robotic and/or surgical devices, systems and methods, particularly for performing telesurgical procedures. It may also be desirable to provide improved techniques for communication among the members of a telesurgical team, and for interfacing with the telesurgical apparatus so as to more fully take advantage of the capabilities of telesurgery to provide enhanced patient outcomes with improved efficiencies. It may be particularly beneficial to avoid unnecessary interruptions and distractions of a surgeon or other system operator, and to avoid delays and/or mistakes in the coordinated activities of a telesurgical team. | ||
| 技术方案 | Medical and/or robotic devices, systems and methods can provide an indicator associated with each manipulator assembly of a multi-arm telerobotic or telesurgical system. The exemplary indicator comprises a multi-color light emitting diode (LED) mounted to a manipulator moving an associated surgical instrument, allowing the indicator to display any of a wide variety of signals. The invention may provide an additional user interface to facilitate communications between the telesurgical system and/or members of a telesurgical team. | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | US8545515B2 | 申请日 | 2009/11/13 |
| 发明名称 | Curved cannula surgical system | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | To further reduce patient trauma and to retain the benefits of robotic surgical systems, surgeons have begun to carry out a surgical procedure to investigate or treat a patient's condition through a single incision through the skin. In some instances, such “single port access” surgeries have been performed with manual instruments or with existing surgical robotic systems. What is desired, therefore, are improved equipment and methods that enable surgeons to more effectively perform single port access surgeries, as compared with the use of existing equipment and methods. It is also desired to be able to easily modify existing robotic surgical systems that are typically used for multiple incision (multi-port) surgeries to perform such single port access surgeries. | ||
| 技术方案 | A robotic surgical system is configured with rigid, curved cannulas that extend through the same opening into a patient's body. Surgical instruments with passively flexible shafts extend through the curved cannulas. The cannulas are oriented to direct the instruments towards a surgical site. Various port features that support the curved cannulas within the single opening are disclosed. Cannula support fixtures that support the cannulas during insertion into the single opening and mounting to robotic manipulators are disclosed. A teleoperation control system that moves the curved cannulas and their associated instruments in a manner that allows a surgeon to experience intuitive control is disclosed. | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | CN104799890B | 申请日 | 2010/11/10 |
| 发明名称 | 弯曲套管和机器人操纵器 | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | 为了进一步减少病人创伤并且保留机器人手术系统的益处,外科医生已经开始执行通过经皮肤的单个切口来研究或处理病人状况的手术程序。在一些情况下,这样的“单端口入路(port access)”手术已经采用手动器械或采用现有机器人手术系统执行。因此,期望的是改进的设备和方法,与使用现有的设备和方法相比,其能够使外科医生更有效地进行单端口入路手术。还期望的是能够容易地修改一般用于执行这种单端口入路手术的多切口(多端口)手术的现有机器人手术系统。 | ||
| 技术方案 | 一种机器人手术系统配置有(多个)刚性的弯曲套管(416a),这些套管延伸穿过同一个开口进入病人体内。具有(多个)被动柔性轴(506)的手术器械(500)延伸穿过这些弯曲套管。这些套管被定向为朝手术部位引导器械。公开了一种远程操作控制系统,该系统以一种允许外科医生体验直观控制的方式移动这些弯曲套管及其相关联的器械。这些柔性轴器械被控制为就好像沿着一条虚拟的直线插入和抽出轴线进行延伸。公开了在该单个开口内支撑弯曲套管的各种端口构件(1402)。公开了在插入到该单个开口以及安装至机器人操纵器上的过程中支撑这些套管的(多个)套管支撑固定件(1902)。 | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | US9358074B2 | 申请日 | 2013/5/31 |
| 发明名称 | Multi-port surgical robotic system architecture | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | A robotic surgery system includes an orienting platform, a support linkage movably supporting the orienting platform, a plurality of surgical instrument manipulators, and a plurality of set-up linkages. Each of the manipulators includes an instrument holder and is operable to rotate the instrument holder around a remote center of manipulation (RC). At least one of the manipulators includes a reorientation mechanism that when actuated moves the attached manipulator through a motion that maintains the associated RC in a fixed position. | ||
| 技术方案 | While the new telesurgical systems and devices have proven highly effective and advantageous, still further improvements are desirable. In general, improved minimally invasive robotic surgery systems are desirable. It would be particularly beneficial if these improved technologies enhanced the efficiency and ease of use of robotic surgical systems. For example, it would be particularly beneficial to increase maneuverability, improve space utilization in an operating room, provide a faster and easier set-up, inhibit collisions between robotic devices during use, and/or reduce the mechanical complexity and size of these new surgical systems. | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | CN105050531B | 申请日 | 2014/3/13 |
| 发明名称 | 具有操控界面的外科患者侧手推车 | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | 移动远程操作的外科系统的患者侧手推车中的一个考虑是患者侧手推车可由使用者容易移动。由于其重量、大小和全部构造,可期望提供患者侧手推车以传动装置以帮助使用者移动患者侧手推车。这样的传动装置可基于来自使用者的输入而被控制,以相对容易的方式移动患者侧手推车。进一步,可期望提供患者侧手推车以控制机构,以驱动和移动不是复杂的而是相对容易使用的患者侧手推车。 | ||
| 技术方案 | 用于远程操作的外科系统的患者侧手推车包括至少一个保持外科器械的操纵器部分和操控界面。操控界面可包括至少一个传感器,其被安置以感测使用者施加的以移动手推车的旋转力、向前力、向后力。操控界面可进一步包括连接机构,以可移除地连接操控界面与患者侧手推车。至少一个传感器可被放置以当操控界面处于与患者侧手推车的连接状态时与患者侧手推车的驱动控制系统信号连通。 | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||
| 公开/公告号 | US6394998B1 | 申请日 | 1999/9/17 |
| 发明名称 | Surgical tools for use in minimally invasive telesurgical applications | ||
| 解决的技术问题 | There are many disadvantages relating to current minimally invasive surgical (MIS) technology. For example, existing MIS instruments deny the surgeon the flexibility of tool placement found in open surgery. Most current laparoscopic tools have rigid shafts, so that it can be difficult to approach the worksite through the small incision. Additionally, the length and construction of many endoscopic instruments reduces the surgeon's ability to feel forces exerted by tissues and organs on the end effector of the associated tool. The lack of dexterity and sensitivity of endoscopic tools is a major impediment to the expansion of minimally invasive surgery. | ||
| 技术方案 | This invention provides surgical tools or instruments for use in minimally invasive telesurgical applications. The instruments typically include a base whereby the instrument is removably mountable on a robotically controlled articulated arm. An elongate shaft extends from the base. A working end of the shaft is disposed at an end of the shaft remote from the base. A wrist member is pivotally mounted on the working end. At least one end effector element mounting formation is pivotally mounted on an opposed end of the wrist member. A plurality of elongate elements, e.g., cables, extend from the end effector element mounting formation and the wrist member to cause selective angular displacement of the wrist member and end effector mounting formation in response to selective pulling of the elongate elements. | ||
| 相关附图 |
|
||

来源:医械知识产权


